Introduction
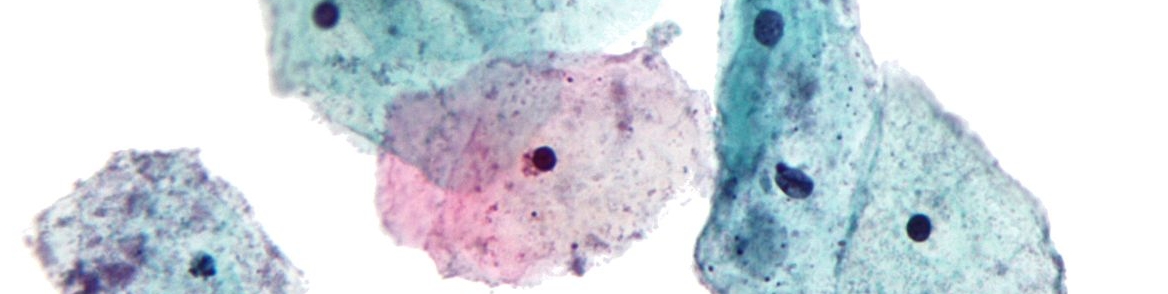
Trichomoniasis is a genital infection caused by protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis. This sexually transmitted disease can affect both genders. Still, the symptoms of the infection are more obvious in women. Men may only complain about slight discomfort inside the penis or burning sensations after urination and/or ejaculation. The discharge is more present in women than in men.
In women, the predilection place of the infection includes the vagina, while in men the urethra is most commonly affected. The discharge varies in color and can be yellow or green and is accompanied by a strong foul odor.
The problem is that many cases of infection remain undiagnosed, and only after certain complications have occurred the patient visits a doctor who then sets the definitive diagnosis.
Possible Complications of Trichomoniasis
Problems with Pregnancy and Infertility
Infertility is only one of the possible complications of trichomoniasis, and it can affect both genders. In women, infertility is caused by pelvic inflammatory disease while in men reduced sperm motility can be a reason for improper fertilization.
In women who are not diagnosed with trichomoniasis on time, the problems in pregnancy may include preterm birth (delivery which occurs before the 37th week of pregnancy). Premature babies can suffer from certain complications. They also weigh less than term babies.
The best way of prevention includes taking vaginal smears before the pregnancy, and if the infection is confirmed a woman is treated with certain medications. After the infection is eradicated she can plan the pregnancy.
Additional complications in pregnant women who are suffering from trichomoniasis include early breaking of the amniotic sac and a high risk of stillbirths. In some cases, the disease can be transferred from the mother onto the baby on its way through the birth canal.
Psychiatric Disorders
- The nationwide population-based study utilized the database of the National Health Insurance (NHI) programme in Taiwan.
- A total of 46,865 subjects were enrolled in this study from 2000–2013, comprising 9373 study subjects with trichomoniasis and 37,492 subjects without trichomoniasis as the control group. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was performed to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) of psychiatric disorders during the 14 years of follow-up.
- Of the study subjects with trichomoniasis, 875 (9.34%) developed psychiatric disorders compared with 1988 (5.30%) in the control group (P?0.001). The adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) of overall psychiatric disorders in the study subjects was 1.644 (95% confidence interval, CI: 1.514–1.766; P?0.001).
- More specifically, the study subjects had a higher risk for developing an individual psychiatric disorder, including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and substance abuse.
- Although metronidazole treatment reduced the risk for developing several subgroups of psychiatric disorders, significant reduction was detected for depression only. Furthermore, refractory trichomoniasis (trichomoniasis visits ? 2) enhanced the risk of psychiatric disorders.
HIV Transmission
According to certain researchers trichomoniasis can increase the risk of getting HIV. People who are suffering from this infection are three to five times more susceptible to getting infected by Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
In women, trichomoniasis leads to inflammation. This inflammation makes women more vulnerable to HIV infection. If a man is already suffering from HIV and Trichomonas vaginalis, at the same time, his semen contains more viruses than the semen of a man suffering only from HIV.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra caused by trichomonas vaginalis most commonly affects men. This urethritis is classified as non-gonococcal urethritis. If left untreated, it can lead to even more severe complications such as epididymitis and infertility.Malignant Tumors
Some scientists have found a connection between trichomoniasis and cervical dysplasia, which is a precancerous change that can lead to cervical cancer.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...