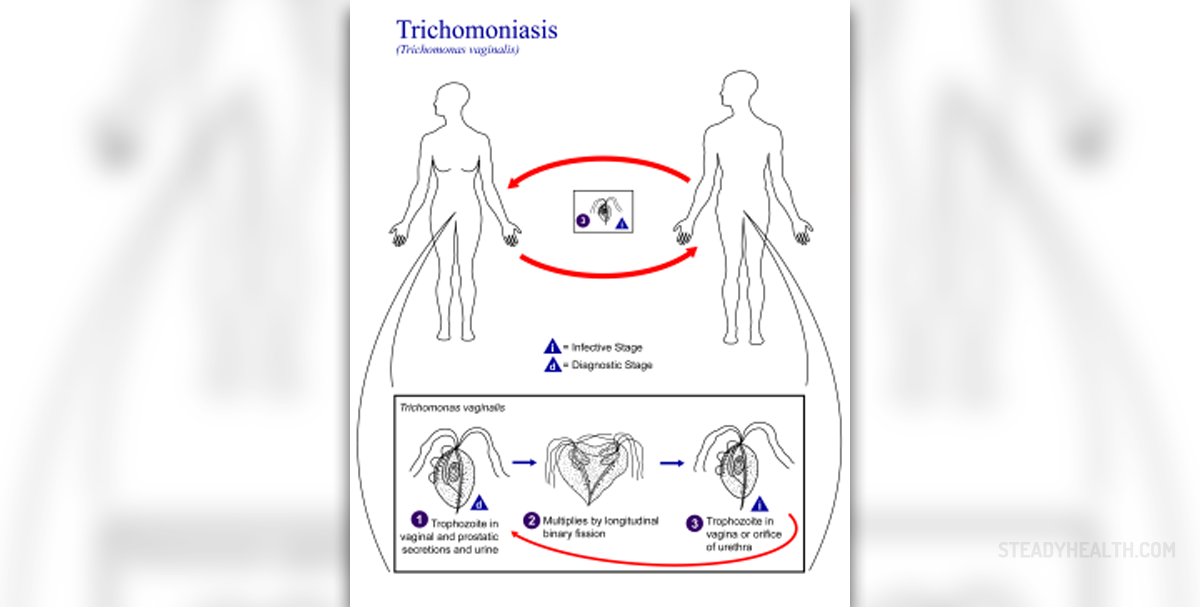
Trichomoniasis is a common infection of the urogenital tract caused by the bacteria Trichomonas vaginalis. The infection is transmitted during the sexual intercourse, when an infected person passes on the bacteria to his or her partner. Trichomoniasis is typical for people who often change their sex partners and do not use protection. A person may also get the infection through wet clothes or towels, through towels that someone used or slightly wet surfaces, such as toilet seats.
Symptoms
Men affected with trichomoniasis usually do not have any symptoms but can spread the infection. The symptoms they can have include painful urination or ejaculation. Women are more likely to get the infection and have symptoms which cause uneasiness and uncomfortable feelings. The vaginal secretions are of yellowish-green color, typically of unpleasant smell. The vagina is red and itchy and can become irritated even more during sexual intercourse. Urination is frequent and painful, the same goes for sexual intercourse. Sometimes, a woman has pains in the lower stomach. The symptoms should be a warning sign for any person to go and see a doctor.
Treatment
As soon as a person notices discomforts and above mentioned symptoms, he or she should turn for doctor's help and start the treatment as soon as possible. Trichomoniasis is a curable disease so there is nothing to worry about in advance. When symptoms appear, medical examinations and tests are done to determine the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis. Doctors usually prescribe medications metronidazole and tinidazole. Both of these medicines are effective if taken in the way directed by the doctor. Partners should restrain from sex as long as the treatment lasts. People with trichomoniasis are more susceptible to other infections, particularly HIV. Topical creams may be used but they are not that effective. Pregnant women are to be careful since the infection may influence development of the fetus. The child is born prematurely or with low eight. Metronidazole should not be used in the first three months.
Prevention
As with any sexually transmitted disease, the best option is to refrain from sex. However, this is easier said than done so here are a few tips on how to prevent infections. Firstly, a person should try to have a long-steady relationship and one partner. Having a promiscuous partner or changing partners increase the risk of getting an infection. Secondly, use of condoms decreases the risk of sexually transmitted disease. Thirdly, never use someone else's clothes, underwear or towels.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...