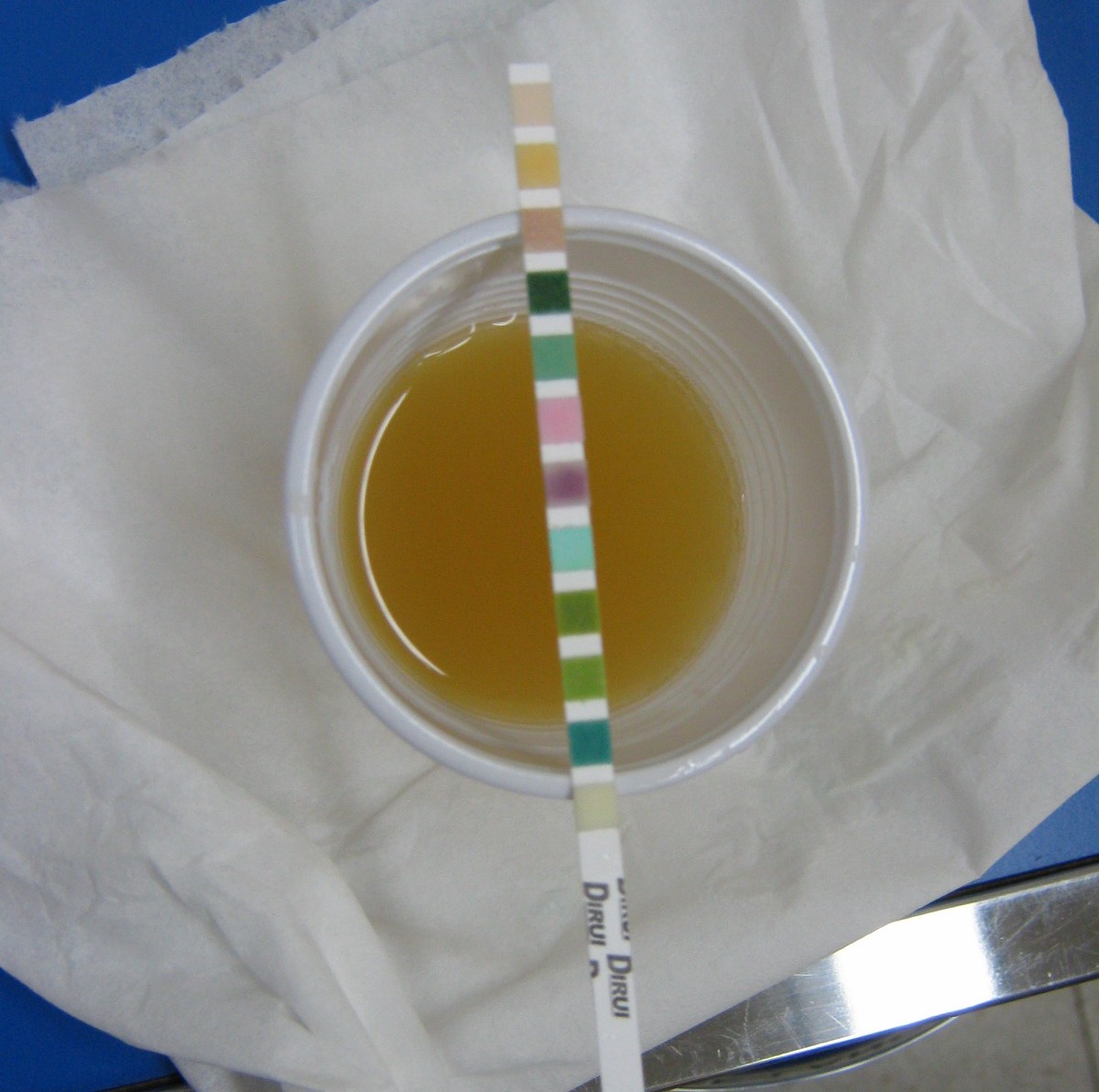
UTI is short for urinary tract infection. Human urinary tract consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Urinary infection usually starts in the bladder and may spread further onto the kidneys. The infection predominantly affects women. This medical condition is rather annoying and can be very painful and frustrating. The person feels constant urge for urination. The act of urination is very painful. The urine may also contain traces of blood. If left untreated bladder infection can spread onto the kidneys and cause pyelonephritis.
Symptoms of UTI
The symptoms and sign of UTI typically include a strong and constant urge for urination, burning sensation during urination, frequent urination with small amounts of urine, strong and unpleasant smell of the urine. Pain which commonly occurs in UTI is in women localized in the pelvis while men usually complain about pain in the rectal area.
If the infection has spread onto the kidneys one may additionally suffer from fever and pain in the lumbar part of the back.
Causes of UTI
UTI usually affects women since their urethra is much shorter than men's urethra. The infection is most frequently caused by certain bacteria including Escherichia coli. These bacteria are normally found in the intestines and close proximity of the urethra and the anus can lead in women to spread of the bacteria and their entrance in the urethra. The bacteria can be also transmitted by sexual intercourse. Apart from Escherichia coli, there are several more infective agents which commonly cause sexually transmitted diseases, and may eventually lead to urethritis.
Treatment for UTI
The infection is confirmed after analysis of the patient's urine. This analysis identifies the bacteria and antibiogram provides with information to which antibiotic the bacteria are sensitive.
The patients suffering from UTI are prescribed antibiotics. They are supposed to take plenty of fluid to 'wash off' the bacteria from the urinary tract. The doctor decides how long the patients must take antibiotics. After the therapy is finished the patient is supposed to give another sample of urine. This will show whether the infection is cured or the antibiotics has failed to eradicate the bacteria.
Simple UTI infections are usually treated with Sulfamethoxasole - trimetoprim, Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin. Patients may be also prescribed analgesics which numb the bladder and relieve certain symptoms of the infection.
Frequent urinary infections may require a longer course of antibiotics. In menopausal women doctor can prescribe vaginal estrogen therapy which reduces the recurrence of the infection.
In severe form of infection patients may need to be hospitalization and given intravenous antibiotics.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...