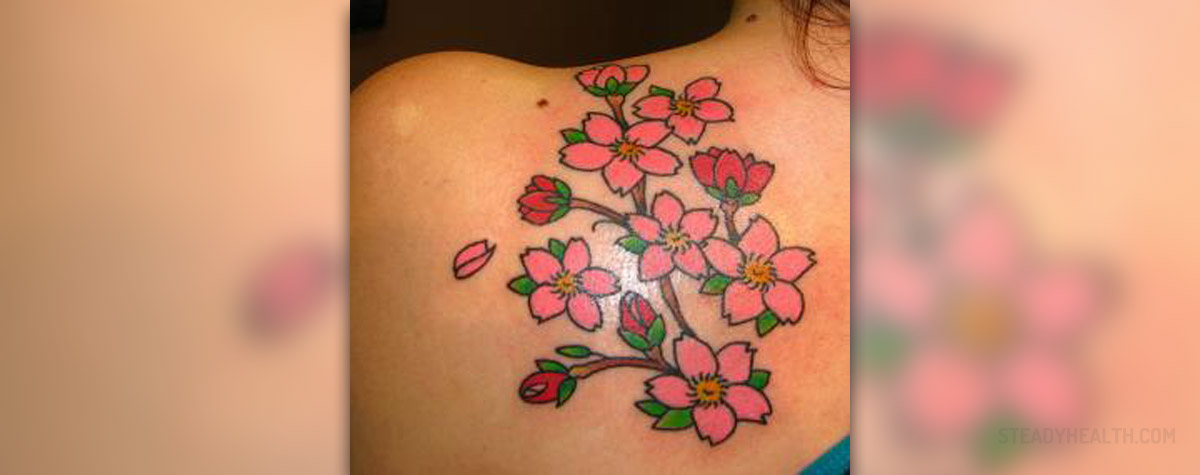

Even though they are present in some cultures for centuries, tattoos seem to be more popular today than ever. They are no longer reserved for prisoners and sailors like our grandparents often think. The number of people with tattoos is probably bigger that we know as they are often hidden beneath the clothes or on unexposed parts of the body.
How a tattoo is done?
Tattoos are permanent designs on the skin that are made with needles and ink, black or in different colors. The needles penetrate the skin leaving tiny droplets of ink in the skin’s top layer. Needles move rapidly and repeatedly allowing the artist to form lines, shapes and shadows.
The process of tattooing may last for several hours, depending on the dimensions of the desired image. It is done without anesthetics and it involves some pain and discomfort. The process normally causes some bleeding, although minimal.
What are the possible complications of tattooing?
Since the needles used for tattooing penetrate the skin, there is a certain risk of infections. If bacteria or other microorganisms affect the skin, there will be some redness, swelling and itching, possibly with pus. However if a tattoo is done professionally and in hygienic environment the risk of infections is not very significant.
Tattoo ink, especially the red colors, may cause allergic reactions. These reactions can occur years after the tattoo is done. The symptom of an allergic reaction is usually a rash.
Scar tissue sometimes develops around the tattoo raising the skin at certain areas. It is also possible for granulomas or small bumps to appear as a reaction to the ink.
Complications are possible during an MRI test. They may include swelling or burning sensation if the tattooed area is being scanned with MRI and the ink may interfere with the quality of the imaging. This particularly goes for people who have very old tattoos, because in the past the dye used for tattooing contained traces of metals like lead.
Blood-transmitted diseases like Hepatitis B and C and HIV virus are possible if the tattoo equipment is not properly sterilized or if the artist uses the same items as for a person with infected blood.
How to prevent complications?
It is vital to be well-informed about the salon and the artist who will perform the tattoo. The salon needs to be perfectly clean and sanitary. The artist must use disposable needles caps and other equipment. Non-disposable items must be sterilized in a device called an autoclave.
The artist must wash their hands frequently and wear protective gloves, which need to be changed for every procedure.
Proper aftercare may prevent complications as well. This means wearing a bandage for the first 24 hours applying antibiotic ointments washing the tattoo frequently with antibacterial soap and avoiding clothes that stick to the skin.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...