This text deals with the complications in the case of a fractured pelvis. The pelvis is an important part of our body that consists of the scrotum and innominate bones (each made of three separate bones).
The function of the pelvis in our body is to protect hollow organs such as the bladder, reproductive organs, and blood vessels. Therefore an injury to the pelvis can cause bleeding from the sacral venous plexus and the bundle of arteries that are in the pelvis.
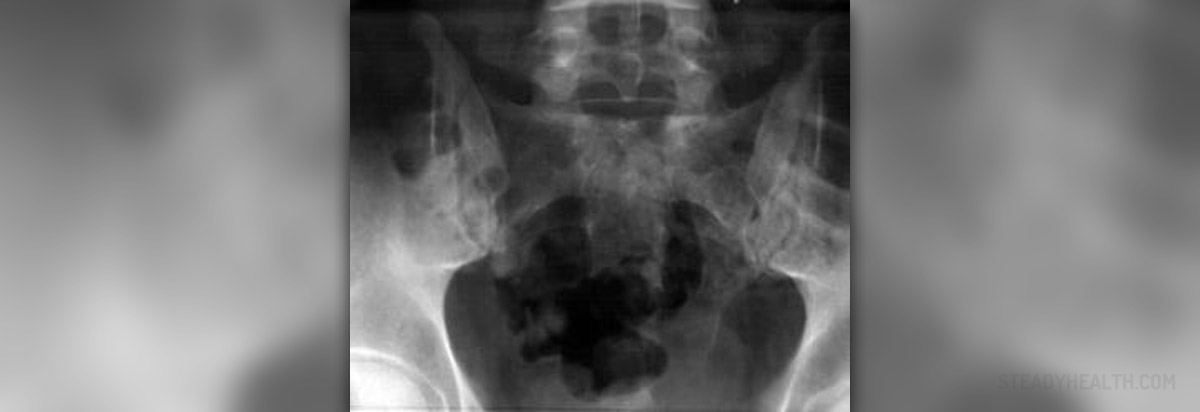
Types of Pelvic Injury
Compression from front to back pelvis – type A injury
Compression from either side – type B injury
Vertical shear injuries – type C injuries
One can suffer from a pelvic injury due to a car accident, a crash, or a fall from a great height, and the result is massive internal bleeding. The bleeding occurs in the pelvis and it is called retroperitoneal hemorrhage. In that way, patients who sustained pelvis injury can lose 2-3 l of blood in a short period of time, and due to the blood loss, a failure of vital organs in the body happens.
The final outcome may be death. In some cases when a fracture of the outer pelvis rim occurs there are no internal bleedings, and this type of injury is not life-threatening and is treated easily.
Complications
- The most common associated injuries are bleeding and retroperitoneal hematoma, intra-abdominal and urogenital injuries, and never injuries in addition to severe pelvic fractures.
- Approximately 12% of trauma patients admitted to Level 1 or 2 trauma centers in the United States exhibit pelvic ring injury, and injuries to intra-abdominal or urogenital organs are present in an estimated 16% of these patients. Prompt diagnosis and effective management of these injuries is essential to a successful outcome.
- A total of 188 cases of pelvic fractures were retrospectively reviewed, and four patients who suffered from four types of rare pelvic fracture complications were described, namely ureteral obstruction caused by retroperitoneal hematoma-induced abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), bowel entrapment, external iliac artery injury, and open scrotal sac injury.
- We demonstrated that combined measures should be employed to prevent the occurrence of ACS following major pelvic fractures. Ureteral catheter support may be a good option at an early stage when ACS occurred. Contrasted computed tomography examination and sufficient awareness are keys to a correct diagnosis of bowel entrapment following pelvic fractures.
- Recognition of risk factors, early diagnosis, and prompt treatment of suspected injury of the external iliac artery are keys to patient survival and to avoid limb loss. Scrotal and/or testicular injury complicated by pelvic fractures should be carefully treated to maintain normal gonad function.
- Additionally, establishment of a sophisticated trauma care system and multi-disciplinary coordination are important for correct diagnosis and treatment of rare complications in pelvic fractures.
Complicationsthat take place immediately after the injury are hemorrhage and shock from the sight of a broken pelvis. The bones may also damage the bladder and urethra, while other injuries such as laceration or perforation of organs that are settled near the pelvis, can appear as the result of a broken pelvis.
If the injury has been exposed for too long, an infection occurs as well as intestinal leakage. Sepsis is possible as well, while thromboembolism may develop due to pelvic injury, meaning the blood clot formed in the pelvis travel through circulation.
There are also a number of complications that can appear after the process of treatment. The result of pelvic injury may be sexual and bowel dysfunction, since men who sustained this type of injury may have difficulty achieving an erection.
If the bones did not grow well, patients may have a problem with sitting, experience pain in the lower part of the back, and gain some extra weight. If there is nerve damage, a sensation can decrease in that area.
Women who have had pelvic injuries may have problems with vaginal delivery. If the injury is connected with the hip, degenerative arthritis may develop as well.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...