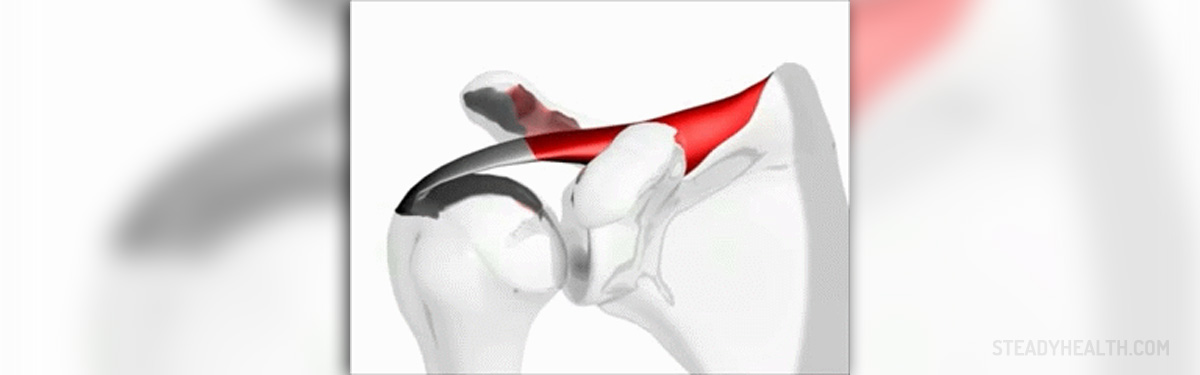
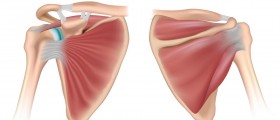
There are a lot of people who suffer from rotator cuff injuries. In most cases, it is the athletes who suffer from it but it is not uncommon for nonathletes to suffer from it as well. Some of the most common symptoms are pain, weakness and decreased range of motion. Just like with any disease, it is important for the problem to be discovered in its early stages for the treatment to be most effective.In most cases of rotator cuff injuries, people will be prescribed with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, a combination of these drugs with acetaminophen has shown excellent results.
Pathophysiology
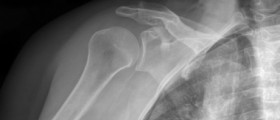
In most cases of rotator cuff tears, they happen due to chronic degeneration and that is why they are so prone to rupture. There are three known stages of tendon degeneration.Stage I is the edema and hemorrhage and it is usually people under the age of 25 who are affected by it.In stage II, people aged between 25 and 40 are affected by fibrosis and tendinitis.In stage III, people older than 50 experience tears of cuff.
Epidemiology
Frequency in the United StatesThere is no strong proof on what the frequency of rotator cuff injuries are. According to some researches, approximately 20 to 30% of people in the United States suffer from rotator cuff injuries. When elderly people are considered, it is thought that 30% of them experience full-thickness tears.
MortalityOnly 4% of all rotator cuff ruptures end up in cuff arthropathy. The chances of a recovery trough the use of conservative treatment plan ranges between 33 and 90%. Elderly people will need more time to recover, however. Surgery is also an option and it can be performed on patients of all ages. Surgery is performed in order for the function to improve.
AgeIt is not common for people under the age of 40 to be affected with rotator cuff injuries. This type of injury is more common with people aged between 55 and 85.The chances of suffering from a rotator cuff injury increase with age.Younger people have a greater chance of suffering from a rotator cuff dysfunction due to overuse and muscle imbalance.
Prehospital careBefore going to the hospital, a person should make the shoulder stable and apply ice packs.
Emergency department careIt is important to reduce inflammation, get rid of the stress in the rotator cuff and correct any biomechanical dysfunction.When there is no need for an operation, a person will need to rest a lot, wear a shoulder sling, receive nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections and follow a basic shoulder-strengthening program. Surgery is a better option for people younger than 60. However, even surgery is not 100% sure of success and the success rate ranges from 77 to 86%.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000438.htm
- medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000358.htm
- Photo courtesy of Young Lae, Moon M.D. Chair of 3D Based Medical Application Working group. Chairman and Professor of Orthopaedics, Chosun University Hospital, Korea by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Shoulder_motion_with_rotator_cuff_(supraspinatus).gif












Your thoughts on this
Loading...