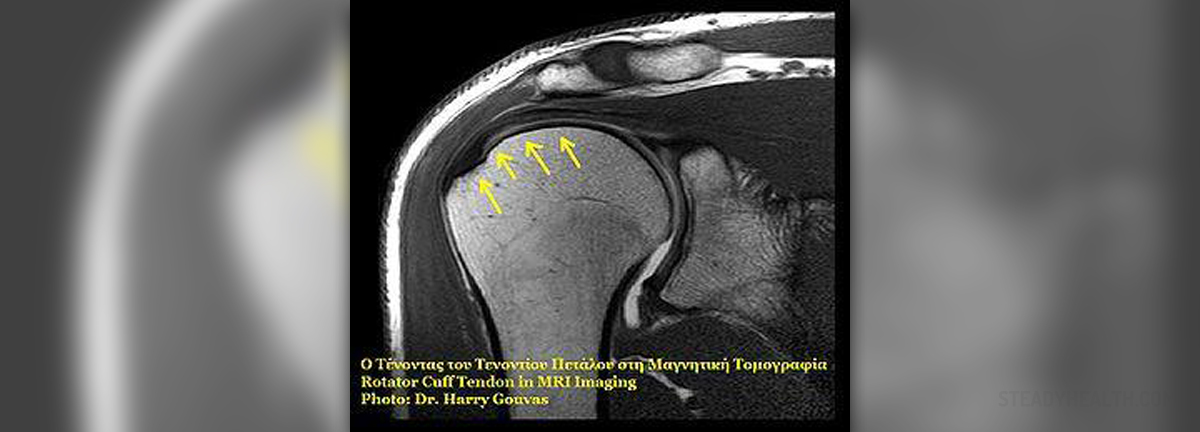
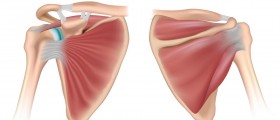
The rotator cuff is a term used for a group of muscles and tendons of the shoulder. Their function is to stabilize the shoulder. Together with two additional muscles of the arm (the teres major and the deltoid) rotator cuff muscles connect the humerus with the scapula. A rotator cuff injury refers to any kind of irritation or damage to any of the rotator cuff muscles and/or tendons.
Clinical Characteristics of Rotator Cuff Injury
This type of injury features with many symptoms and signs including pain and tenderness in the shoulder area, shoulder weakness and loss of shoulder range of motion. The pain intensifies during certain movement such as reaching overhead, reaching behind the back, lifting, pulling and even while sleeping on the injured side. In the case of severe injury patients complain about persistent pain (pain that occurs during movement and at rest).
Causes of Rotator Cuff Injury
There are numerous causes of rotator cuff injury. For example, the injury may develop in a form of tendinitis, inflammation of one or several tendons. The inflammation develops as a result of overuse or overload. It is typical for athletes. Apart from tendinitis bursitis is another form of injury of rotator cuff muscles. In this case the inflammation affects the fluid-filled sac that lies between the tendon and the skin or the bone.
Rotator cuff injury is most commonly a consequence of normal wear and tear and occurs in people older than 40. Degeneration of the rotator cuff structures is a predisposition for an injury. Furthermore, the injury is associated with poor posture, falling or lifting and pulling. Repetitive stress is also one of many causes of inflammation and potential tearing.
Therapy for Rotator Cuff Injury
Minor injury requires proper rest, application of cold and hot compresses, pain relievers and exercise therapy (physical therapy). The exercises are deigned to assist in healing, improve the flexibility and strength of the injured muscles.
Furthermore, in moderate and severe forms of the injury patients may be treated with steroid injections or surgery. Direct injection of corticosteroids in the injured area reduces inflammation and pain. Surgery for rotator cuff injury is performed only in the case of a large tear. The open repair can be obtained through a longer or a shorter incision. The repair may also be performed arthroscopically (with an assistance of a small camera). Patients who have additionally developed rotator cuff arthropathy may need more extensive surgery such as partial shoulder replacement or total shoulder replacement. And finally, even after surgery patients with rotator cuff injury must undergo physical therapy.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000357.htm
- medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000358.htm
- Photo courtesy of Dr. Harry Gouvas, Greece by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rotator_cuff.jpg









Your thoughts on this
Loading...