How common are rotator cuff injuries?
These are very common and it could be said that this is the most common type of shoulder injury, frequent in all age groups. Injuries may vary from the relatively simple inflammation of the tendons in the rotator cuff to far more serious tears, where the tendons of the rotator cuff were actually torn from the bone. Typically, tendinitis is the problem of the younger population, while tears affect people in their middle ages and the elderly.
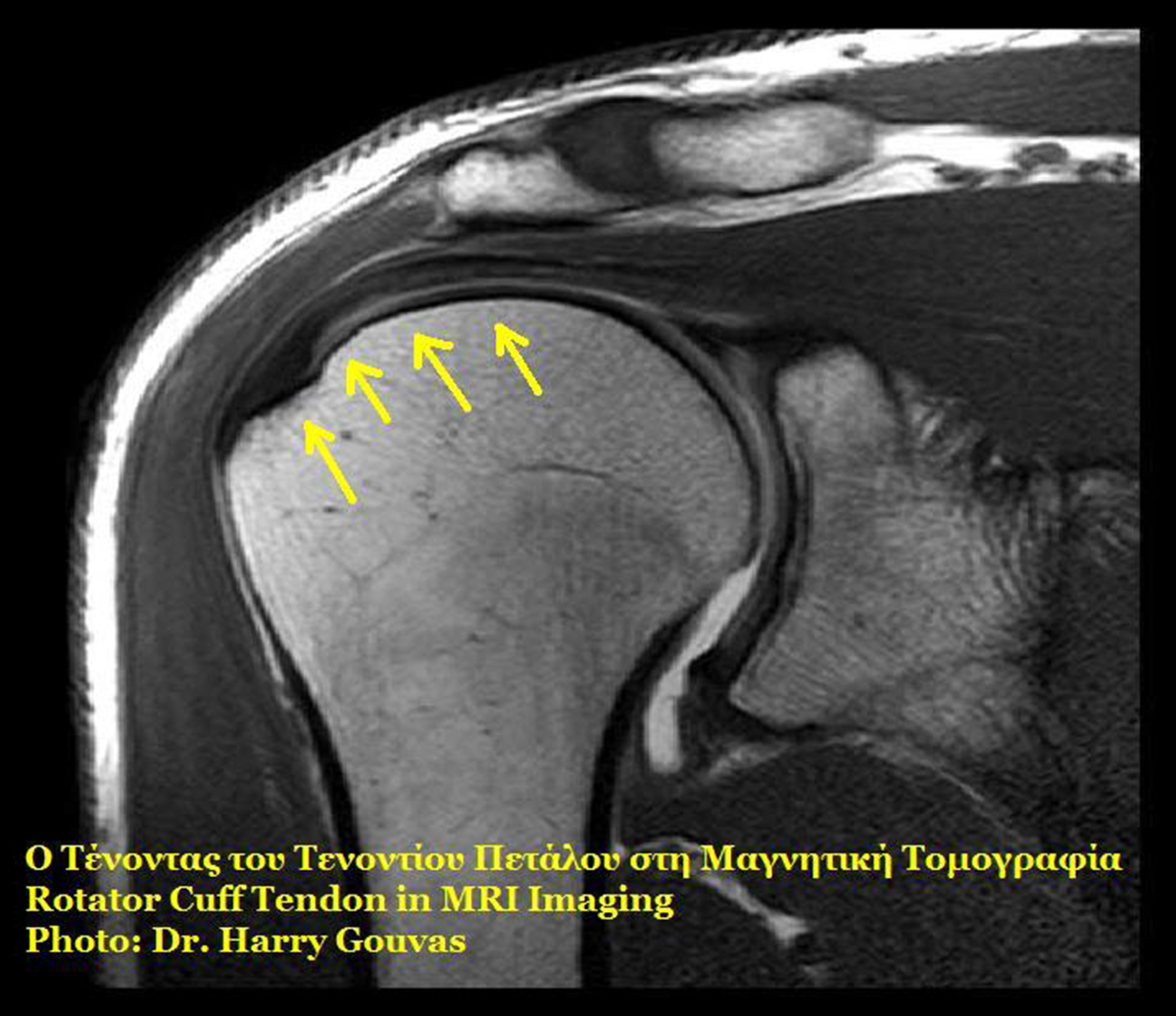
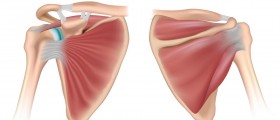
But what is a rotator cuff? To put it simply, it is a complex envelope made of four muscles and their tendons that encloses the shoulder joint. Shoulder joint is very complex, as it has a large degree of freedom of motion. Muscles and tendons by which they attach to the corresponding bones are therefore arranged in a complex manner that allows such motion. To be precise, the rotator cuff is responsible for lifting the arm overhead and rotating it to the side.
How dangerous is rotator cuff tear?
This is condition where the ligament physically detached itself from the bone. This means that the muscle whose ligament was torn can no longer operate. It can contract and relax, but it does not pull the corresponding bone when it contracts. It would be similar to trying to open the door without holding onto the doorknob. The torn ligament cannot stick back to its proper place on the bone by itself, and surgery is required to resolve this. Rotator cuff tear is recognizable by pain in the shoulder, particularly overnight, and weakness of the arm when you try to lift it above your head. these problems are virtually debilitating, and, like it was told, there is no other option but surgery to fix this.
Diagnosis
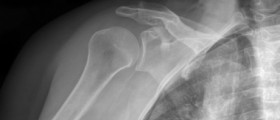
Pinpointing a rotator cuff tear can be done by a number of methods. It may suffice to hear what happened when the problems began. Of course, X-ray scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are much more reliable, but at times arthroscopy of the shoulder is required for exact diagnosis.
Arthrowhat?
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure. It uses as small of an incision as possible in order to see inside the operating field by means of a miniature camera (as in diagnostics), as well as to operate by specialized instruments. There is more to arthroscopy than fewer and less visible scars. Normal musculature and shoulder tissue in general is less disturbed by arthroscopy than by open surgery and there is less pain in the postoperative period. Recovery time remains the same as with open surgery as the torn tendons heal at their own rate regardless of the method used to reattach them to the bone. Surgery can be done using regional or general anesthesia and can be done on an outpatient basis.
What after the surgery?
An immobilizing sling for the operated arm is required for up to a month so that the tendons can heal undisturbed. Patients are not allowed to use their own muscle power to lift their own hand for four to six weeks. But, a physical therapist works with the patient at that time. The goal of physiotherapy is to use the shoulder joint without using the muscle.
This means that the physiotherapist will move your hand for you. Recovery to full strength takes up to two years. It is important to exercise the operated shoulder continuously.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...