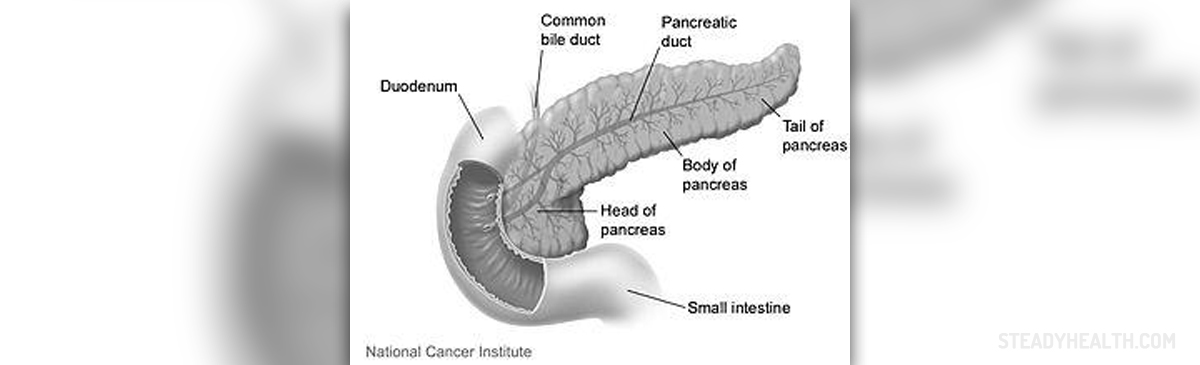
The beginning of the small intestine is called the duodenum. Once this part of our body gets inflamed, the condition is referred to as duodenitis, manifesting through abdominal pain, bleeding and numerous other signs. Helicobacter pylori is the most common trigger of duodenitis, since it triggers infections in the area.
Information on Duodenitis
The above mentioned bacteria commonly infects people at a young age. However, signs of an infection do not appear until adulthood. When they do appear, duodenitis is one of the possible scenarios. If this inflammation is not treated timely, it often evolves into duodenal ulcers.
As for triggers of duodenitis, tobacco and alcohol abuse, overuse of non- steroidal anti-inflammatory medications or Crohn's disease, all belong to the list of possible culprits. The symptoms of this inflammation may vary from one person to another. Nevertheless, if triggered by H. pylori, the symptoms will remain prevalent until proper treatment takes place. Many times, duodenitis is asymptomatic. On the other hand, it can frequently manifest through abdominal pain and burning, nausea and vomiting.
The most common treatment for this condition includes antibiotic medications. Yet, if the bacteria is not triggering the infection, reducing stomach acid levels may help. Naturally, personal hygiene increase, lifestyle modifications and dietary changes may be necessary for a successful treatment of duodenitis.
If you happen to experience severe abdominal pain, accompanied by bloody or excessively dark stools or vomits, seek medical assistance immediately.
Signs and Treatments for Duodenitis
Along with the previously mentioned symptoms of this condition, bloating, appetite loss, blood in stool or vomit can all be added to the list. Take this state of affairs seriously and seek medical treatment as soon as the symptoms become this severe.
Duodenitis is commonly treated by medications. As for antibiotics, tetracycline, metronidazole, amoxicillin or clarithromycin may be used. Proton pump inhibitors are also a helpful group of medications including rabeprazole, lansoprazole, Omeprazole, esomeprazole and pantoprazole. Finally, histamine H2-receptor antagonists may be involved in duodenitis therapy too, predominantly, cimetidine, famotidine, nizatidine and ranitidine.
Also, if you happen to experience vomiting along with your duodenitis problem, you are highly advised to replenish your electrolyte and fluid loss by drinking plenty of water, adding a bit of sugar and salt to it.
All in all, duodenitis can be successfully dealt with if the treatment begins timely. If this is not the case, the condition may escalate, triggering numerous other health problems, making the whole matter much harder to cope with.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...