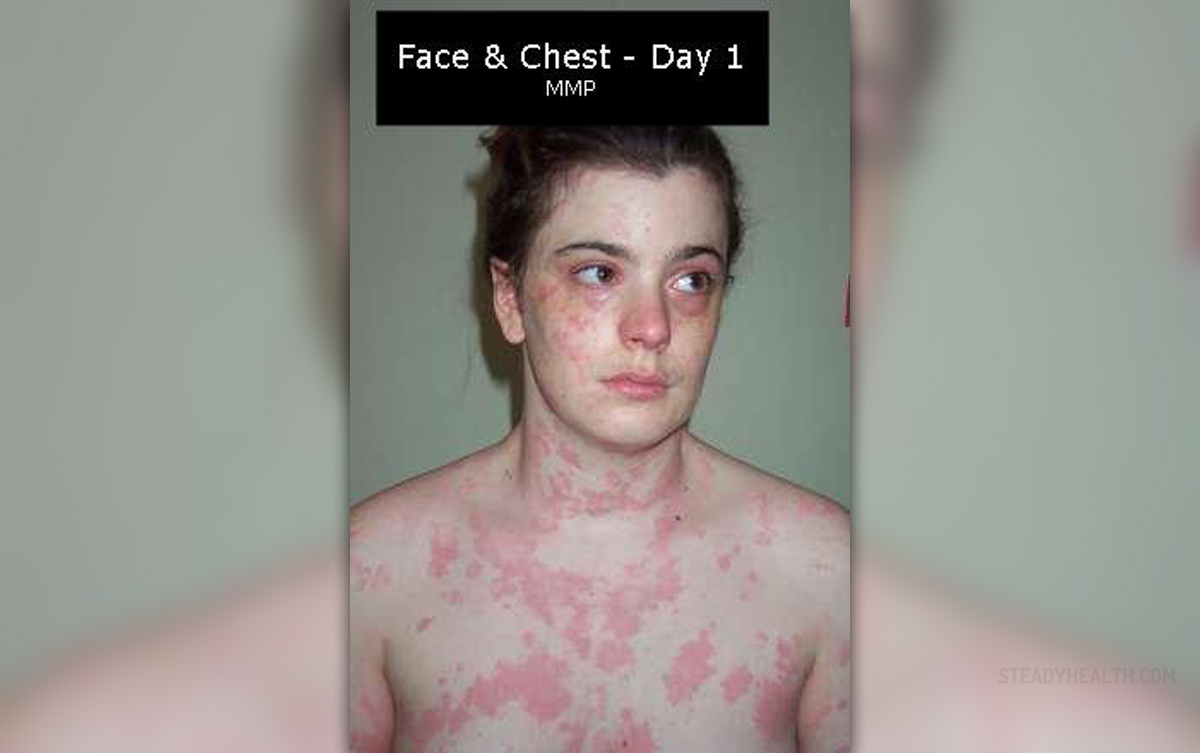
Chronic hives can be defined as a skin rash, with batches of red or white welts, being raised and usually itchy, appearing and disappearing frequently, without ever really going away. Most cases of hives come and go, never to return. However, with chronic hives, or urticaria, the skin changes stay present for more than six weeks, reoccurring frequently. Usually, the reason behind this condition is some sort of autoimmune disease, even though in most cases people never find out what causes their rash.
Signs of Chronic Hives
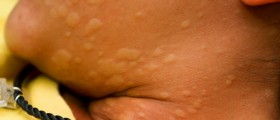
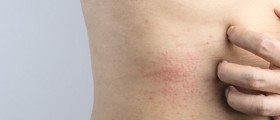
Chronic hives may appear as small rings, wheals or greater patches of affected skin. Red flares may accompany an itch that usually goes hand-in-hand with hives. Face is the most common area where chronic hives occur, even though other parts of the body may be susceptible as well.
More Facts Regarding Chronic Hives
Chronic hives may bother you for 30 minutes or even up to 36 hours, once a single breakout takes place. Sometimes, these can appear in the throat and affect a person's capability to breathe, requiring immediate medical assistance. Even though there may be no triggers for chronic hives, some people have experienced this condition breaking out when they expose their bodies to heat or stress.
Medical Assistance and Chronic Hives
Since chronic hives can be a sign of something more serious like an underlying illness, it is best to seek medical assistance as soon as you notice that you are suffering from this condition. Moreover, seek help immediately if hives are severe or do not respond to any kind of treatment, bothering you for more than several days. Additionally, consider feeling lightheaded, suffering from respiratory problems and having your throat swollen signs of danger.
What May Lead To Chronic Hives?
Chronic hives is inflammation of the skin which happens due to certain cells releasing histamine into the bloodstream, leading to leakage from small blood vessels. Lupus or a thyroid disease are common underlying illnesses, triggering chronic hives. Nevertheless, you may also develop this condition as a reaction to certain food, environment or other situations you are in. Finally, medications can have chronic hives as a side-effect.
If you know what triggers your chronic hives, stay away from it. This can mean avoiding certain kinds of food or drinks, environments, materials etc. You can benefit from keeping a food diary. This way, you will be able to track down your chronic hives and the food you have been eating. Also, if medications are causing this problem, change them or stop taking them completely.


-Causes,-Symptoms-And-Diagnosis_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...