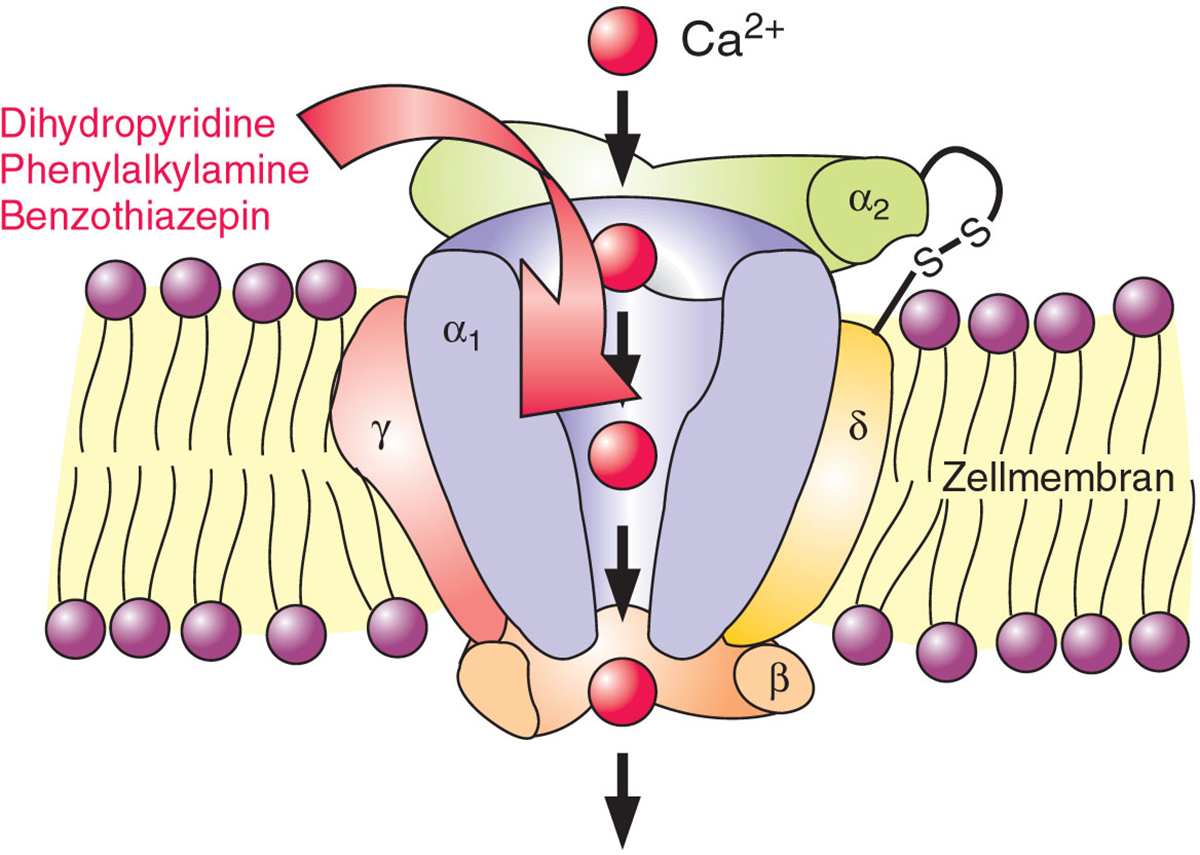
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers are the group of medications used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). These medications are also known to be helpful in the medical conditions when there is a need to widen the arteries, such as arrhythmias, angina, cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension, brain hemorrhage, and Raynaud’s syndrome. Sometimes, patients suffering from migraines, heartbeat problems and brain aneurisms might be suggested to use calcium channel blockers too.
Studies have revealed that this group of medications provide the best treatment of high blood pressure in African American people. For other patients suffering from hypertensions, beta blockers and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) are proven to work better.
This group of drugs work by preventing the entry of calcium into muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels. Calcium is necessary for the muscle cells contraction so calcium channel blockers relax (or dilate) the blood vessels. Relaxation is the process that leads to decrease of blood pressure. In the heart, these medications lower the contractility, which is actually a force that makes heart muscle cells contract. So, the effect of calcium channel blockers to the heart is the decrease of cardiac output, and the total effect to the body is lower high blood pressure.
Some of the well known calcium channel blockers are: diltiazem, verapamil, amlodipin and nicardipin. These medications are differentiated by the duration of the action and effects they have to the heart and blood vessels.
Adverse Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers are usually well tolerated in patients and don’t cause severe side effects. In some rare cases there might be some serious consequences.
The most common side effects include: nausea, headache, extreme decrease of the blood pressure, heartburn, constipation, sleepiness and lightheadedness. Some of the calcium channel blockers patients experience swelling of the legs, caused by the fluid buildup or edema. Other problems may be: swollen and bleeding gums, abdominal upset and pain, gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hot flushes.
Severe side effects of these medications are: breathing and heartbeat problems, allergic reactions and yellowing of the eyes and the skin. Calcium channel blockers may even cause a liver disease. Any of these side effects should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Calcium channel blockers are known to interact with other medications and food. There is an increased risk of side effects if you are using these medications with alcohol, lovastatin, simvastatin and carbamazepine, or when eating grapefruit.
Pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers should always consult their doctor about the use of calcium channel blockers.











_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...