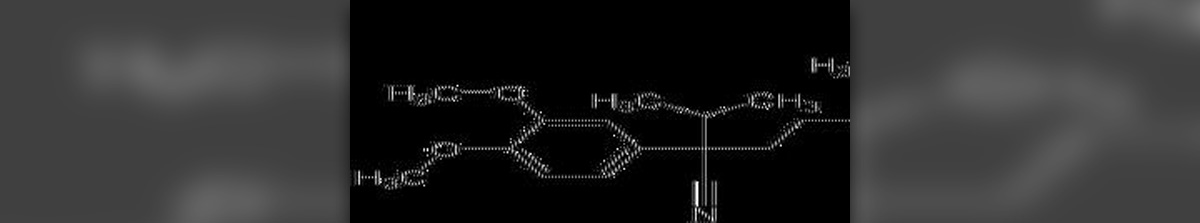
Human heart needs certain amount of oxygen to be able to perform the job of pumping the blood. Inadequate amount of oxygen is, therefore, known to cause heart pain (also known as angina). Calcium channel blockers (or CCBs) are drugs used to dilate the arteries and make the pumping of the blood easier. This way, the heart does not need so much oxygen and the pain stops.
Indications for Calcium Channel Blockers
CCBs are medications useful for the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure), angina pectoris and also for the therapy of certain abnormal heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. These drugs can also be given to patients who had a heart attack and cannot tolerate other drugs like beta blockers. CCBs are also useful for post-heart attack protection in patients with angina or atrial fibrillation. Although these drugs are used after a heart attack, studies showed no protection from repeated heart attack or mortality in these patients.
When comparing CCBs with ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitors, these drugs are similarly efficient regarding hypertension treatment but still unable to prevent kidney failure due to high blood pressure or present diabetes mellitus.
Calcium channel blockers can also be helpful for treatment of pulmonary hypertension, cardiomyopathies, subarachnoid bleeding or Raynaud’s syndrome, as well as for prevention of migraine headaches in some patients.
Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions
CCBs are known to cause side effects as many other drugs. Patients using these drugs may complain about nausea, headache, constipation, skin rash, swelling of the legs and low blood pressure. Some of them also experience drowsiness and dizziness due to the use of CCBs. In certain number of patients, there is gum overgrowth and liver dysfunction as a result of treatment with calcium channel blockers. All medications used to manage hypertension (high blood pressure), including CCBs are known to be the cause of sexual dysfunction in some patients.
Additionally, diltiazem (Cardizem) and verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) can worsen symptoms of heart failure, decreasing the pumping of the blood from the heart. These drugs are also considered to interact with many other medications, especially due to decreased elimination of drugs by the liver. Because of that, patients using statins such as atorvastatin, lovastatin or simvastatin, as well as carbamazepine should be very careful about the potential toxic effects.
Grapefruit juice is also known to interact with calcium channel blockers and a single glass (200ml) of this juice can significantly raise concentration of these drugs in the serum. Doctors, therefore, recommend taking grapefruit juice at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after administration of CCBs.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...