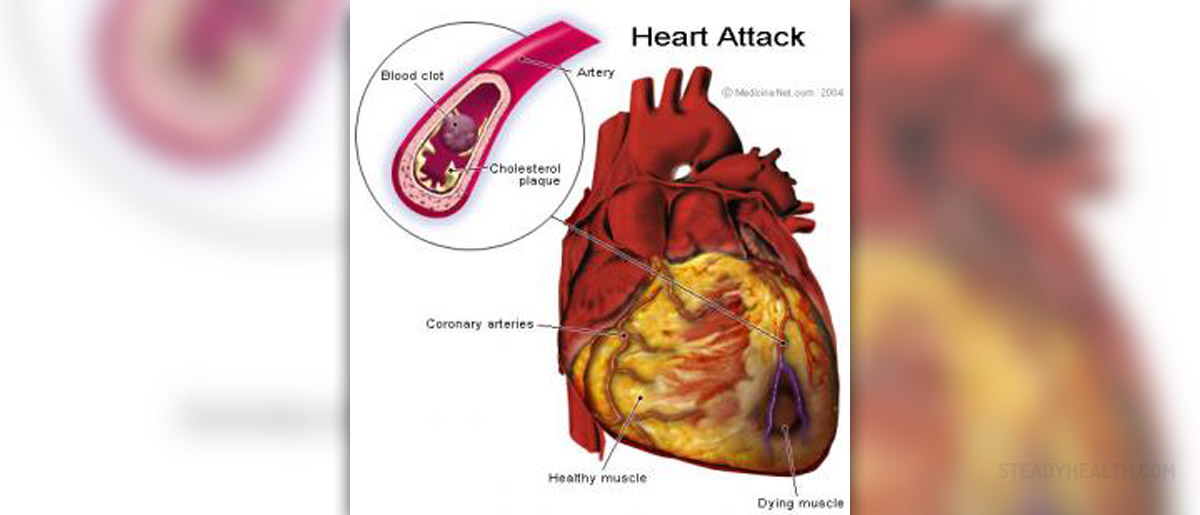
Heart attack medically termed myocardial infarction is among the leading causes of deaths around the world. Elderly people are usually struck with the heart attack mainly because the fatty material that forms the blood clots accumulates over the years. The heart attack is sudden interruption of a blood flow to the heart due to the blockage in some part of the heart. The heart is not supplied by the needed oxygen and as a result, it stops functioning. The complications of the heart attacks include: Atrial fibrillation, cardiogenic shock, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, abnormal heart rhythms, rupture of the heart wall, chest pains, pericarditis.
Symptoms
The upper chambers of the heart send signals to the chambers vital for pumping the blood into the body. Heart attack can overload the upper chambers, atria and as a consequence the heart rate increases making it difficult to control the supply and pumping of the blood. The condition is called atrial fibrillation when the heart may fail. Blood clots are likely to occur that are able to move to some other organs, brain for example and cause stroke.
The heart attack leaves the person lethargic, confused with a low blood pressure, heart dysfunctions and inadequate blood flow through the body which may affect the kidneys and cause discomforts there. This so-called cardiogenic shock is one of the major reasons for deaths. A person receives medications and possibly is inserted an intraaortic balloon pump that helps regulate the blood pressure in the aorta, enabling better blood flow from the heart to the body.
The heart attack causes damage to the electrical activities inside the heart. The heart starts beating at irregular rate and rhythms which is termed arithmias. The heart muscles are greatly affected by the heart attack, so if the left ventricle is impaired there is the great likelihood of getting congestive heart failure. The blood supply to the body is poor, which can be treated by medications or by placing the bypass. Sometimes the heart walls may break apart which highly increases the risk of eventual death. The hole that can be formed in the muscle between the left and right chamber can be surgically corrected but it is essential to perform the operation as soon as possible. The fatal outcome is highly probable if the outer wall of the heart ruptures, causing the blood to spread outside the area of the heart.
Heart attacks lead to the inflammation of the pericard so people feel pains in the chest while breathing, sneezing, coughing, and breathe heavily. The blood flow is slowed down by the heart attack so the patients often feel the chest pains.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...