
Carbohydrates
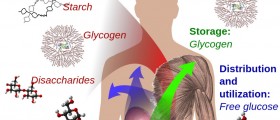
Carbohydrates are a source of energy and are stored in glycogen (muscles and liver) from which they can be easily released, giving the energy to the body. This energy is needed for performing all physical activities and maintaining important body functions (heart rate, respiration and other chemical processes in cells and tissues). 50% of energy in the body derives from carbohydrates, 25% from fat and 25% from proteins. 1 g of carbohydrate from food releases energy of 4 kcal (17 kJ).Starch and sugars are broken down into simple sugars by the enzymes in the body. They are reabsorbed in the small intestine and passed into the bloodstream and liver, where they are converted into glucose.
One part of glucose supplies the brain, nervous system and muscles with energy, while the other part is converted into glycogen (energy reserves), which is located in the liver and muscles. Once the reserves are filled, the remaining part of glucose turns to fat stored in the adipose tissue.
Sources of carbohydrates are bread, pasta, rice, cereals, fruit, vegetables, milk, dairy products, sugar and sweets.
Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar
Glycemic index shows how much certain carbohydrate increased glucose level in blood after digestion.Simple carbohydrates (glucose, fructose) and foods such as honey, white sugar and white bread, fall into carbs with high glycemic index - larger than 50. They are characterized by rapid entering the bloodstream and raising blood sugar level, causing increased secretion of the hormone insulin and releasing energy quickly due to its simple molecular structure.
In contrast, foods such as rice, pasta, bananas, apples, brown bread, chickpeas, dried apricots, squash, beans, dried figs, energy drinks and energy bars, have a low glycemic index - less than 50. Complex carbohydrates, which need, due to complex molecular structure, more time to decompose and turn into simple sugars, slowly enter the bloodstream and increase the concentration of sugar in the blood, gradually increase secretion of insulin and provide energy over a longer period.
To ensure long-term energy, it is necessary to consume complex carbohydrates, while simple sugars should be taken just before major physical effort such as an additional source of quick energy in athletes.
Carbohydrates of plant origin contain fiber cellulose and hemicellulose (insoluble in water) and pectin, gum and resin (water soluble). The fibers in the body cannot be broken down and used as a source of energy, but they are very important in human diet. Foods rich in fiber are whole grains, cereals, vegetables, fruits and seeds.
Benefits of Food Containing Dietary Fibers
Dietary fibers are the indispensable ingredients of the modern man diet. They positively effect on digestion - absorb water in the intestines and kidneys, increase the volume of stool, enhance peristalsis of intestine, accelerate its discharge and thus prevent constipation. It is advisable to consume at least 25-35 grams of fiber a day.Food rich in fibers speeds up the passage of food through the intestine, thus accelerating the removal of potentially harmful substances.
They contain negligible amounts of fat, so fibers are recommended for losing weight.
Small amounts of soluble fiber before physical activity can prevent a sudden drop in blood sugar.
Whole grains (dietary fibers insoluble in water) help in preventing diseases of the digestive tract such as hemorrhoids, constipation and colon cancer. Diet containing fresh fruits, legumes and oats (dietary fiber soluble in water) helps in normalizing insulin secretion, reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and obesity.



_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...