
Basal Metabolism
Basal metabolism (sometimes also known as basal metabolic rate or BMR) is the minimal number of calories you need to take to provide the daily energy for your body if you were to sleep 24 hours a day. This energy is necessary for the function of all organs in the body, such as heart, brain, liver, kidneys, lung, etc.
Metabolic Factors
BMR is affected with aging, amount of the muscles, physical activity, medical and mental condition and requires strict circumstances at the time of the measurement. There is also a resting metabolic rate (RMR), which is more common and measured much easier than BMR.
BMR factors include:
Age, Body surface, Body temperature, Diet, Fat percentage, Gender, Genetic predisposition, Outside temperature, Physical activity.Metabolism is genetically predisposed. Some people have faster and other slower metabolism rate. Men have more muscles, less fat in the body and therefore have 10 to 15% faster metabolism than women. Every decade after the age of 20 BMR gets down by 2%.
The way your body looks affects the metabolism. The heavier you are, your BMR will be higher. Also, body surface area (the height and the weight) affect the metabolism – tall and thin people usually have higher BMR. Percent of the body fat is associated with the BMR – less fat means faster metabolism.
Dieting can seriously affect the metabolic rate. Low calories diets might decrease BMR for 20 to 30%.
Physical exercise helps in building the muscles, which require much more energy than the fat tissue and thus increasing metabolic rate.
Body temperature and external temperature increase the BMR. A person with fever (42 C) will have a 50% higher metabolism than someone with normal body temperature. Long term exposure to heat also has uplifting effects to the metabolism.
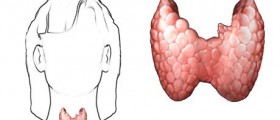
Thyroxin is the hormone of the thyroid gland which regulates the metabolism. In the case of overproduction of thyroid gland, BMR could rise up to 200%.
How to Calculate BMR
BMR is the most important factor of the metabolic rate and it determines how many calories you need to take in to lose or gain some weight. The accurate values of BMR and RMR can be measured using calorimetry and gas analysis. There are also equations that include age, sex, weight and height, which can roughly estimate the metabolism.
TDEE is total daily energy expenditure and includes the energy your body requires to function for 24 hours with all of your daily activities. This is actually a maintenance level of your metabolism, and it should be the starting point of any diet.
The average TDEE is about 2000 calories for women and 2800 calories for men. Extremely physically active people and athletes have much higher demand for energy, and their TDEE might go up to 6000 calories a day.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...