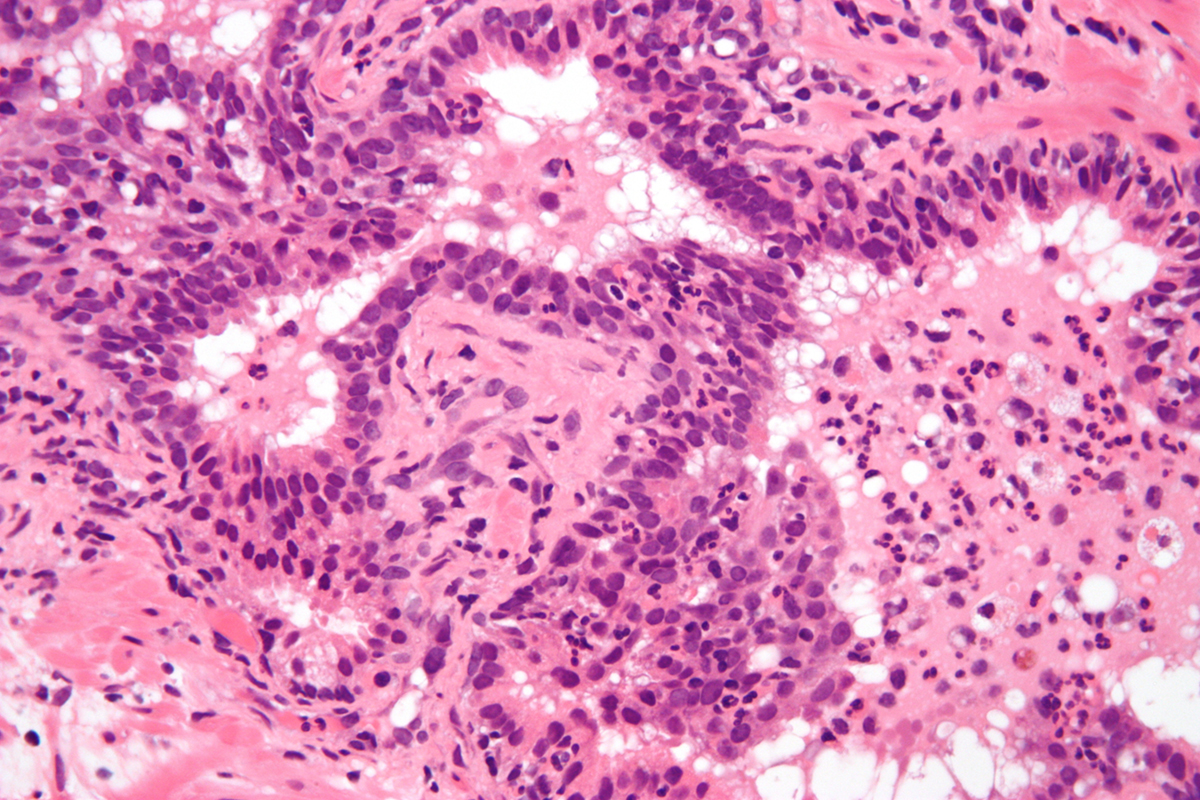
Acute prostatitis, which is rarer than chronic prostatitis, is an infection of the urinary tract in men, involving the prostate. Bacterial prostatitis is, as the name suggests, caused by the bacteria, and it is the most common form of acute prostatitis.
Acute bacterial prostatitis
Prostate is an exocrine gland that is a part of the male reproductive tract. It is located between the bladder and the rectum and its role is to secrete an alkaline fluid that makes about one third of the semen. Its alkalinity serves to counteract the acidity of the vagina and to make the environment more suitable for the sperm.
Prostatitis is a condition in which there is a large number of inflamed cells in the prostate, which can be of infectious or inflammatory origin. It can be acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic abacterial and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacteria, in most cases by a single strain. However, in some cases prostatitis can be caused by two or more different bacteria strains.
The bacteria which most commonly cause prostatitis are gram-negative bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family. These can include E. coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiela, Enterobacter and Pseudomonas aaaeruginosa. E. coli or Escherichia coli is the most common among these.
Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis is almost never asymptomatic. Upon the onset of the condition, the person suffering from it is likely to experience fever with chills, pain in the lower back and in the groin, frequent urge to urinate, especially during the night, with small amounts of urine and a general feeling of weakness and fatigue. The patient may also experience muscle and joint pain.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is based on clinical findings through physical exam, and also through laboratory tests of urine, which, in bacterial prostatitis, should confirm the presence and the nature of the bacteria. Most doctors will also order blood tests, which usually show an increased number of white blood cells, as a response to the infection. The physical exam may include rectal palpitation of the prostate, which is usually enlarged in patients with acute bacterial prostatitis. However, doctors must be careful not to massage the prostate vigorously, because it could lead to sepsis, which is very dangerous.
Treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis consists of antibiotic medications. It is important to establish which type of bacteria is responsible for the infection, in order to be able to prescribe adequate antibiotics. Some antibiotics work particularly well for prostatitis, and those include doxycycline and Ciprofloxacin, among others.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...