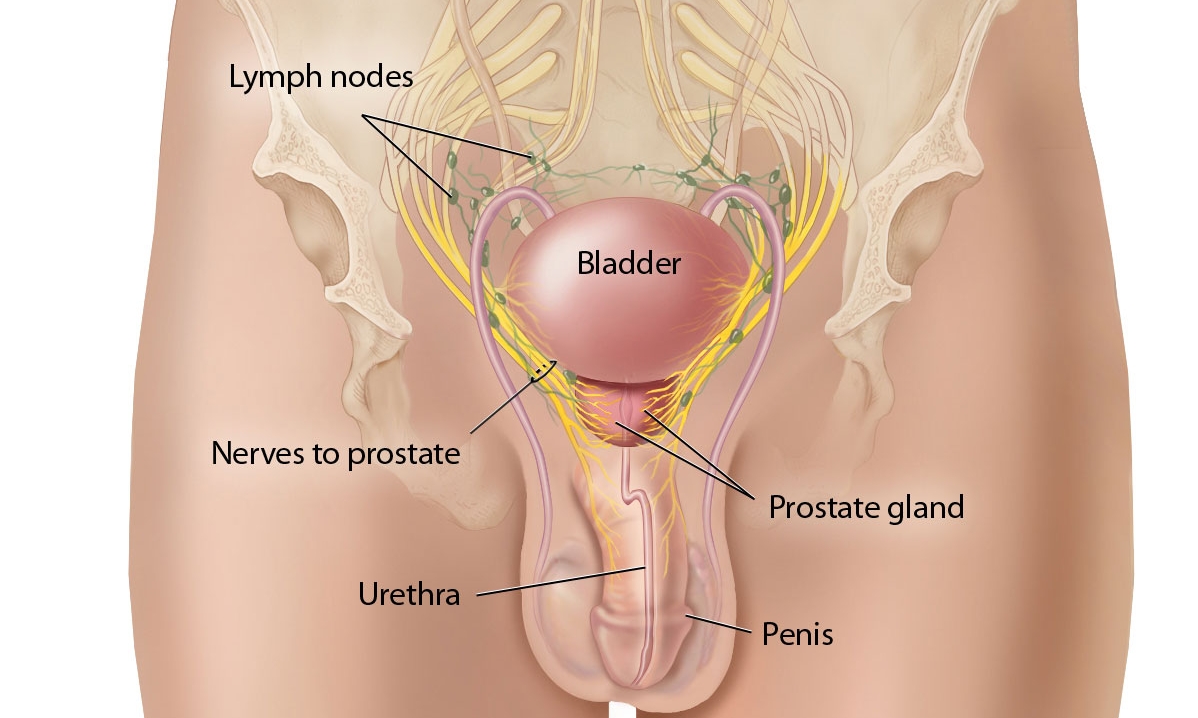
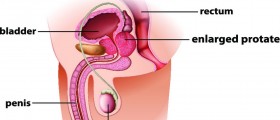
Prostate glands and prostatitis
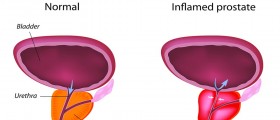
Prostatitis is the medical term for the infection of the prostate glands, which are right below the gallbladder in men. In the majority of cases, prostatitis affects men above 50 years of age, even though it can also affect younger males. Prostatitis or the prostate infection can be divided into four types: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic nonbacterial prostatitis and prostatodynia.
Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis
This type of prostate infection is the easiest to diagnose, because only the urine needs to be checked for the presence of bacteria and white blood cells. It is treated with antibiotics. The most common symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are pain in the genitals, lower back pain, frequent and painful urination, bad urine odor and difficulty in bowel movement.
Symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is not a common condition and should be treated promptly since it can spread to the bladder. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is marked by recurring infection or inflammation, which usually indicates that the prostate malfunctions. Antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines are used in the treatment of this type of prostatitis. The common symptoms of this condition include frequent urgency to urinate, painful urination, pain after the urination, pain in the lower back and testicular pain in the genitals, as well as pain in the joints and muscles.
Symptoms of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is among the most common types of prostatitis and can cause infertility in men. There are several symptoms that can warn about the presence of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis and they include pain in the genitals, pain with ejaculation and burning sensation while and after urination. The men with this type of prostatitis may also have difficulty with bowel movement.
Symptoms of prostatodynia
Another name for prostatodynia is chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Antibiotics are used to treat this type of prostatitis, although they are not very effective since they cannot completely eliminate the root cause of the problem (there is no visible bacterial infection in the prostate or the urinary system).
The men who suffer from chronic pelvic pain syndrome may experience pain in the pelvic region, pain during ejaculation and lower back pain. Furthermore, the common symptoms of this condition are also impotence, urgency for urination and fever. However, if the blood appears in the urine or in the semen, it can be a warning sign of prostatodynia.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...