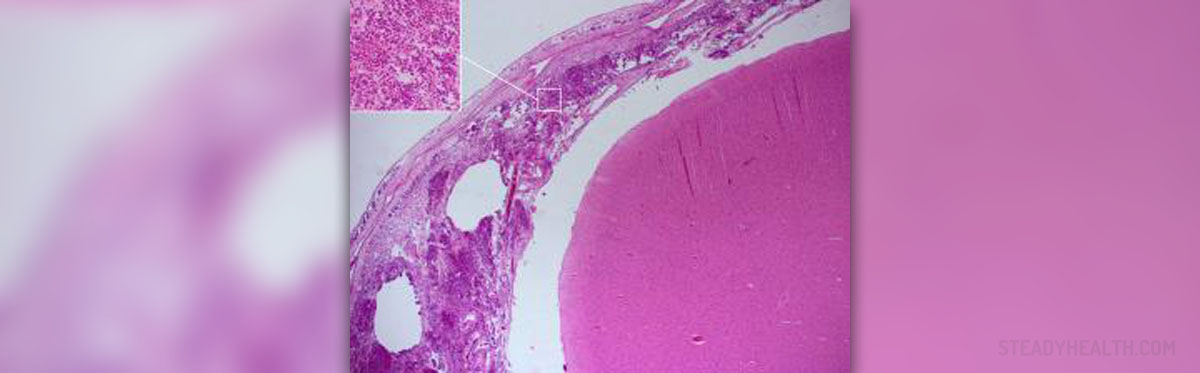
Meningitis is a serious medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the meninges – the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This condition is potentially life threatening, and it is always considered a medical emergency. The reason behind this classification is that inflamed meninges can affect the brain and the spinal cord, leading to severe complications. Various things can cause meningitis. Most commonly, it results from an infection with bacteria or other microorganisms.
Causes of acute bacterial meningitis
Bacterial meningitis is caused strictly by bacteria. Different types of bacteria are associated with this disease, and the exact causal species usually vary by age group. In very small children and premature babies, meningitis usually occurs from the infection with group B streptococci, which is normally found inside of the vagina. These young patients are also endangered by Escherichia coli or Listeria monocytogenes, which are normally found in the digestive tract.
Older children are at the higher risk of Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The same bacterial species account for 80 percent of all cases of bacterial meningitis in adults. The elderly population is at the highest risk of infection by L. monocytogenes.
In some cases, bacterial meningitis can occur not from the systemic infection but from a recent trauma to the head. Damaged scull may become exposed to the bacteria from the nasal cavity, and the inflammation of the meninges can occur. Patients with a cerebral shunt, cochlear implants for hearing loss, or similar device, are also at the higher risk of developing infection.
Symptoms of acute bacterial meningitis
The most common symptom of meningitis is a severe headache and stiffness in the muscles and neck. Patients can also experience sudden high fever, changes in mental state, and extreme intolerance to bright light or loud noises. In small children, the symptoms can be completely absent and the child may only seem irritable and looking unwell. Infants younger than 6 months will normally develop a bulging on the top of the head, abnormal skin color and have very cold extremities.
Treatment of acute bacterial meningitis
Treatment for bacterial meningitis is available, but it will be successful only if a diagnosis is established on time. Bacterial meningitis is typically treated with a number of effective antibiotics. Antibiotics must be started immediately and doctor will usually recommend a treatment, even if the results of preliminary tastings are not yet complete. When the results of CSF culture become available, doctor may switch to specific antibiotic therapy tailored especially to the specific causative bacterium and its sensitivities to antibiotics.









-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)




-and-Multiple-Sclerosis-Differences-And-Similarities_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...