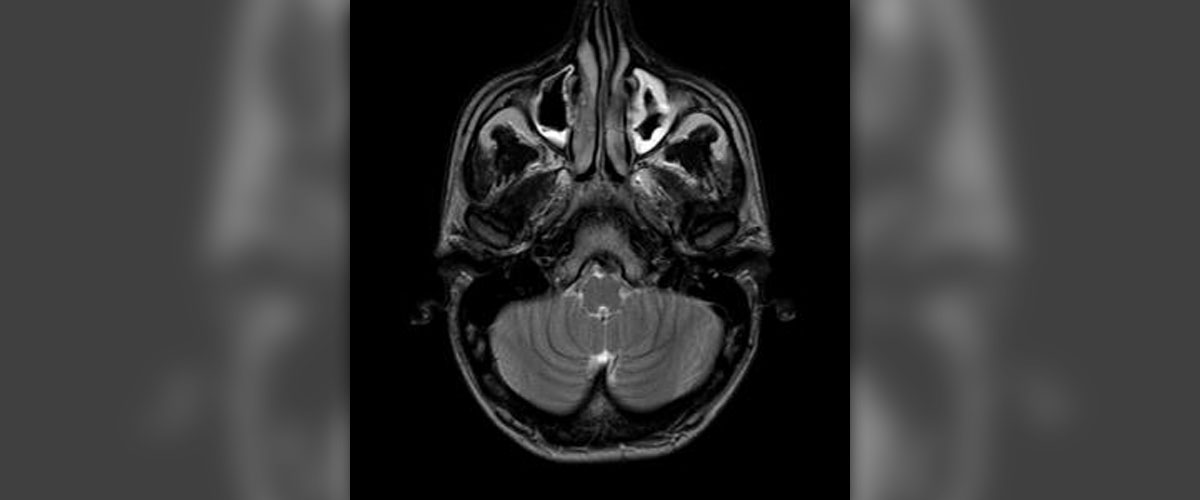
Acute bacterial sinusitis is an acute inflammation of a sinus, a cavity in the skull. The infections is, as the name suggests, caused by bacteria and it may linger up to 4 weeks. There are several sinuses in humans (ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal and maxillary) and each of them can get inflamed. In many cases acute bacterial sinusitis develops as a consequence of cold or allergy attack as well as irritation caused by environmental pollutants.
In case the infection lasts longer than 6 weeks it is classified as chronic. It is estimated that acute bacterial sinusitis develops as a complication of 2% of all cold infections.
Clinical Characteristics of Sinusitis
The initial symptoms and signs are those associated with the primary condition, the preceding condition of sinusitis. So, initially patients complain about symptoms and signs of common cold, allergy or irritation caused by pollutants. Once bacteria have entered the sinuses (secondary infection) the person develops headaches and facial tenderness (the affected sinus is particularly tender to touch). Nasal secretion (that was initially transparent and serous) becomes thicker and changes color into green or yellow. Coughing and sneezing are two more characteristics of acute bacterial sinusitis. Patients also develop a fever (body temperature rises above 38°C), bad breath and due to postnasal drip the throat becomes sore. In case of maxillary sinusitis the pain is located on either side of the nostrils and in the cheek bones. And finally, there are additional symptoms and signs of upper respiratory infection and in some cases the infection may spread to the ear.
What Bacteria Cause Acute Bacterial Sinusitis?
In majority of cases of acute bacterial sinusitis the culprits of infection are Pneumococcus, Hemophilus influenzae, Moraxella, Streptococcus species and Staphylococcus. Prior to bacterial infection in many cases patients develop viral infection of the upper respiratory tract and infection caused by bacteria develops as secondary.
Treatment for Acute Bacterial Sinusitis
Acute bacterial sinusitis is successfully treated with antibiotics. It is essential to choose the most powerful antibiotic and to take medications as they are prescribed, never skip doses and finish the entire course. In case the person does not respond to prescribed antibiotic he/she must be given a suitable substitute antibiotic since there is a chance that bacteria are resistant to the first drug that has been administered. Additional help is obtained from nasal sprays or drop decongestants. They relieve nasal decongestion, make breathing much easier and accelerate drainage from the affected sinuses. With proper treatment up to 90% of all acute sinusitis is cured. Unfortunately, some people suffer from recurrent sinus infections and in these cases there is chance of infection to become chronic.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...