After any kind of injury that leads to loss of integrity of the skin and the underlying tissues the body engages reparation processes which eventually lead to wound healing. All the damaged tissues are at some point restored. Wound healing is quite a complex process and goes through several stages. The process of healing starts immediately after the injury and the length of the process depends on several factors. It is obvious that smaller wounds heal much faster comparing to severely damaged tissues that require some time to completely restore.
What Are Stages of Wound Healing?
The very process of wound healing goes through several stages including the inflammatory phase, the proliferative phase, the remodeling phase and finally, epithelization.
The inflammatory phase starts immediately after the injury. Since damage to the skin or underlying tissues generally leads to bleeding, in order to stop the excessive loss of blood the body sends signals that cause narrowing of the affected blood vessels and formation of clots that will close the damaged parts of the vessels. This phase leads to production of many inflammatory factors. During the inflammatory phase debris is removed with the assistance of polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages. These cells are essential for wound healing.
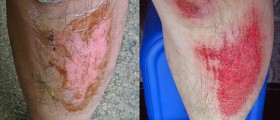
The proliferative phase features with formation of cell latticework or matrix accumulation. The entire phase includes formation of new skin cells as well as new blood vessels that pervade the matrix. Newly formed blood vessels give the wound specific red or pinkish color. They supply the wound with all the nutrients necessary for the process of restoration.
The remodeling phase includes organization of collagen that has been synthesized during the proliferative phase. Collagen gives the strength to the wound and its presence reduces the intensity of the red color of the wound that is characteristic for the proliferative phase.
Epithelization is the final stage of wound healing. The wound is covered with new epithelial cells and the new skin covers the damaged area.
Additional Information
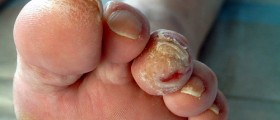
It is essential to mention that only superficial and small wounds may heal on their own without forming large scars. This is not the case with severe damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Deep cuts, burns as well as severely damaged tissues require proper cleaning and surgical care. Some wounds require stitching or stapling (which helps the distant parts of the wound to come closer and heal properly without significant scarring). Furthermore, severe burns require skin grafting. The doctor will chose the most appropriate approach that will accelerate the healing and reduce the chance of excessive scarring.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...