
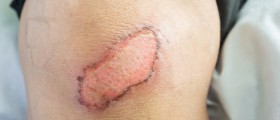
Wound dehiscence is a medical term for separation of the edges of the surgical incision line after they have been sutured. This is considered as a postoperative complication and must be treated as soon as possible. Wound dehiscence is related to poor wound healing and it usually does not occur spontaneously. On the contrary, it is most commonly caused by certain factors such as poor knotting or grabbing of stitches, trauma to the wound and obesity. It also affects people suffering from certain medical conditions more than healthy patients.
Wound dehiscence basically occurs around 7 - 10 days after the surgery. It is a serious complication which may additionally cause several more complications including infections or even death.
Causes of Wound Dehiscence
Wound dehiscence may be associated to many factors and illnesses.
It is typical for people suffering from Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. These patients have a genetic disorder and are simply not capable of producing collagen which is an essential component of scars. Furthermore, proper collagen synthesis is possible only if there is a sufficient amount of vitamin C. This leads to conclusion that wound dehiscence occurs more in people suffering from scurvy, the deficiency of vitamin C. People suffering from diabetes mellitus as well as those with pulmonary disease are more susceptible to wound dehiscence. This also refers to people with poor nutrition supply.
Apart from the previously mentioned wound dehiscence also occurs in patients who have undergone radiation therapy (if this form of treatment is applied on the particular area of the body which is later operated), those suffering from cardiovascular diseases, anemia, cancer, alcoholism and jaundice. And finally, patients who are suffering from cough or constipation and have undergone abdominal surgery may eventually end with wound dehiscence caused by increased intraabdominal pressure.
Treatment for Wound Dehiscence
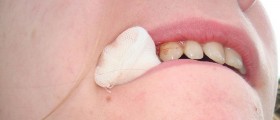
The wound dehiscence treatment involves packing of the wound. This is achieved with excessive sterile gauze. Once the wound is packed the package is protected with a tape. Patients are administered antibiotics in order to prevent infection of the wound. It is essential to change the wound dressing as frequent as possible. This is another way of preventing infections. After several days the wound may be exposed to air which accelerates the process of healing.
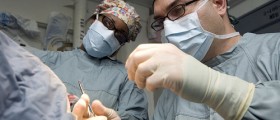
If there is contaminated, infected or even necrotic tissue the surgeon must perform revision of the wound and remove the damaged tissue. The wound is then re-stitched. In some cases a temporary or permanent piece of mesh is placed onto the dehiscence to bridge the gap between edges of the incision line.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...