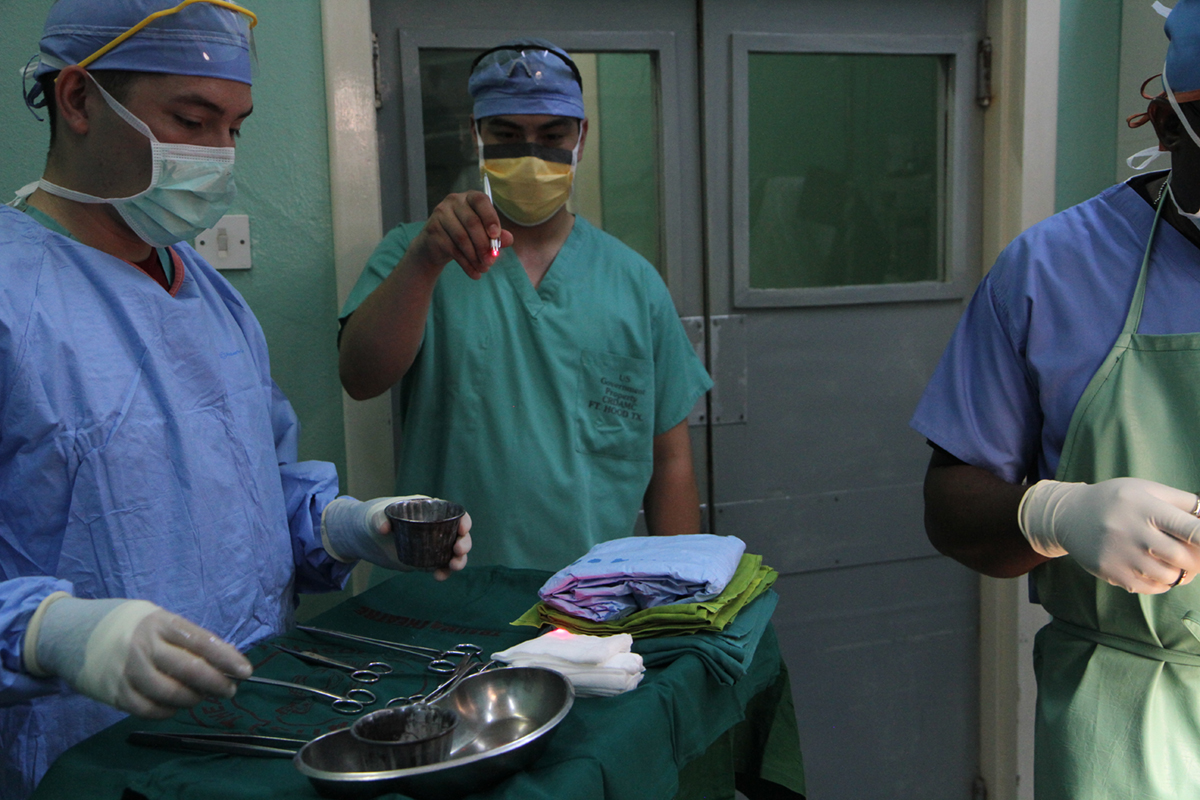
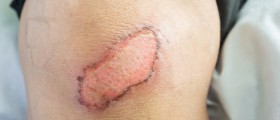
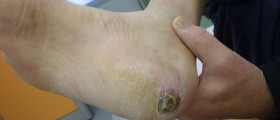
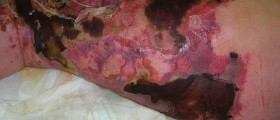
Wound Debridement
Wound debridement includes removal of infected, damaged and necrotic tissue. This can accelerate the process of wound healing. There are several techniques which are used in wound debridement. They include surgical debridement, mechanical debridement, autolytic debridement, enzymatic debridement, chemical and biological debridement.
Why is it done?
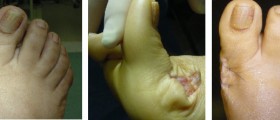
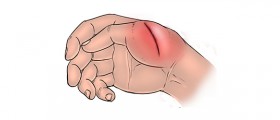
Proper assessment of an ulcer or other open wounds can be achieved only after all the dead tissue has been removed. Presence of necrotic tissue contributes to infection and consequent sepsis. Necrosis significantly interferes in process of healing. Namely, it is highly suitable for the growth of bacteria, particularly anaerobes, and it causes excessive inflammation which induces systemic release of cytokines which boosts septic response. Dead tissue also interferes in scarring since it does not allow the wound to close properly. Because of all the previously mentioned it is highly important for all the necrotic and gangrenous tissue to be completely removed by debridement.
Wound Debridement Procedure
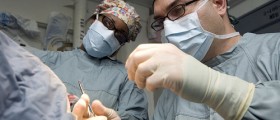
The surgeon will decide for the best possible debridement technique. It is essential to explain all the details regarding debridement to the patient.Patients either undergo general or local anesthesia depending on the size of the necrotic tissue which needs to be removed. General anesthesia is given to patients who undergo excessive debridement. In some cases, even spinal or epidural anesthesia can be applied.
In surgical debridement a team of surgeons participates in the procedure. Prior the surgery every little detail needs to be properly assessed. It is important to determine the nature of the necrotic tissue and the best type of debridement, whether there is a risk of infection and if there is risk patients are administered antibiotics, the chance of underlying processes, the full extent of the dead tissue, the relation of the wound and surrounding structures.
There are possible complications of debridement and the leading one is excessive bleeding. It does not occur so often. The surgeon is due to stop with debridement in case the anatomy of the wound and surrounding structures is not clear enough and the structures cannot be properly recognized and if heavy bleeding occurs especially if the source of bleeding is unclear.
After debridement the wound is covered in a gauze bandage. It is additionally covered with a loose gauze dressing. Postoperative care of the wound is essential for proper healing. The wound must be covered with dry dressing which can control bleeding. After certain period of time surgeons may recommend moist dressing to accelerate the process of healing. The procedure is generally successful. However, in some patients debridement needs to be repeated.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...