
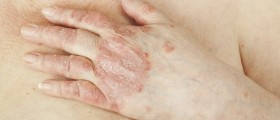
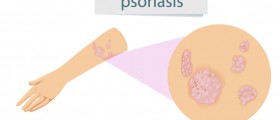
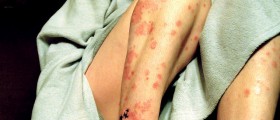
Psoriasis is one of many skin disorders frequently associated with emotional stress and discomfort. This is a chronic immune-mediated condition characterized by skin redness, irritation and scaling. The affected skin develops characteristic appearance which is a consequence of an overproduction of the skin cells located in the outer layer.
Psoriasis Causes
The actual cause of psoriasis still remains mystery. However, many scientists believe that the condition develops as a result of dysfunction of the immune system. Namely, human immune system produces a specific type of leukocytes called T cells. These cells are engaged in defense against different diseases and infections. In people suffering from psoriasis there is excess of T cells in the skin. They are blamed for excessive production of skin cells and subsequent silvery flaking of the skin in individuals suffering from this skin condition.
Genetic connection
Furthermore, there may also be a genetic connection to the condition. The disease is proven to run in some families. Today scientists are studying families with many members suffering from psoriasis. They are trying to identify genes that may be associated with the disease. They believe that there is genetic predisposition to psoriasis and that only once a person is exposed to some triggers, the condition develops.
Psoriasis is not contagious and usually goes through periods of flare-ups and remission.
Psoriasis Pathophisiology
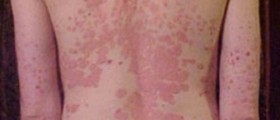
Skin cells normally regenerate every 28 days. This way the old cells from the very surface shed and are replaced with new ones. In people suffering from psoriasis this regenerative process occurs frequently and the skin cells regenerate every 2-4 days. So, there is not enough time for all the old skin cells to shed, they remain and accumulate on the skin's surface and eventually form thick, silvery, scaly patches known as plaques. Apart from excessive skin cell regeneration there is also increase in the blood vessels in the affected skin areas. This explains why the affected skin under plaques is more red comparing to the healthy, unaffected parts.
Psoriasis Clinical Characteristics
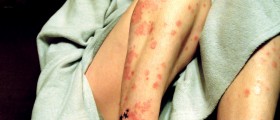
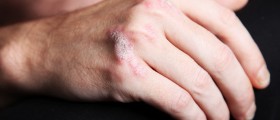
Patches or plaques are or different shape and size. They are very itchy and may be sometimes a source of burning sensation. If they form around the joints, the skin may be additionally affected by cracks.
In majority of cases psoriasis affects the scalp, elbows, knees, face, lower back and sometimes event palms and soles. In some individuals apart from skin the condition is also associated with inflammation of joints. This is a so called psoriatic arthritis.
Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis is brought under control with medications that inhibit production of skin cells. These drugs may be administered alone or in a combination with several more treatment options like light therapy, climatotherapy as well as stress reduction therapy.
Scales are removed with the assistance of moisturizers, sunlight and salicylic acid. More complex forms of the disease are treated with psoralen plus UV-A light, UV-A light alone, acitretin, retinoids and more potent drugs such as methotrexate, infliximab, Cyclosporine, alefacept and etanercept.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...