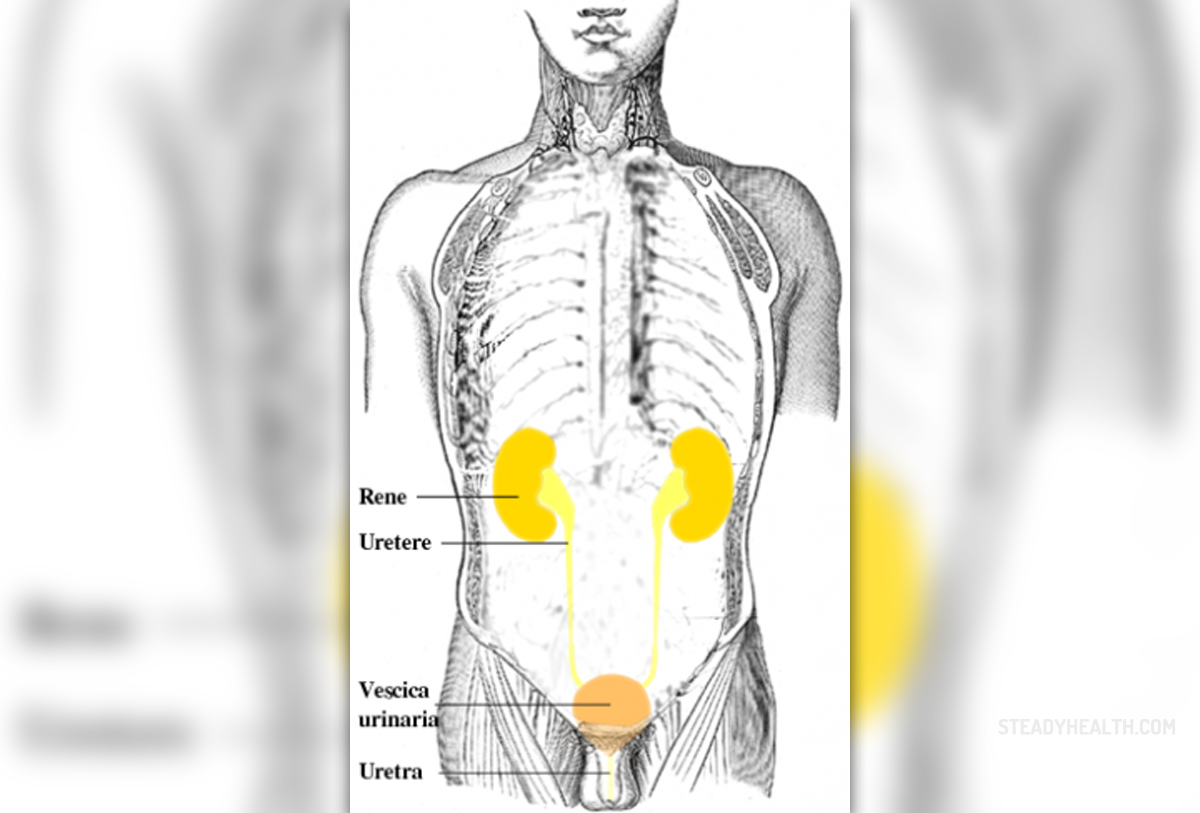
A urinary tract infection or UTI is an infection that affects one or more parts of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is composed of kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra. Urine is made in the kidneys, it passes to the bladder through ureters and then exits the body through the urethra.
Urinary tract infections usually affect the lower parts of the tract, and those that travel upwards, towards the kidneys, are called pyelonephritis.
Causes of urinary tract infections in men
The causes of urinary tract infections in men and women are basically the same. Bacteria enter the tract through the urethra and travel towards the bladder. The most common bacterial cause of UTI is E. coli.
There are certain factors that increase the risk of getting a UTI. For example, abnormal formation of the tract often leads to problems. Vesicoureteral reflux and neurogenic bladder often carry the risk of recurring urinary tract infections.
If there is a blockage in the urinary tract, it prevents the normal flow of urine and when the urine stays inside the tract for long, the bacteria multiply and cause infections.
Men who are not circumcised are believed to be more prone to UTI than those who are.
Prostate problems and weak immune system also increase the risk of having an UTI.
In addition, urinary tract infections can be contracted through sexual intercourse.
Signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections in men
One of the most common signs of UTI is frequent urination, urge to urinate when there is little or no urine to be passed, waking up at night to go to the bathroom.
People who have a UTI will most likely feel pain or pressure in the lower abdomen, have foul smelling urine, traces of blood in urine and fever.
Diagnosis and treatment
Upon hearing about the patient’s symptoms and complaints, a doctor will do a physical exam and perform tests that will diagnose the UTI. A sample of urine will be sent to the laboratory and examined, checking for the presence of bacteria. Blood tests will also be done.
In some cases, imaging tests will need to be done, especially if doctors suspect the infection has progressed to the kidneys.
As for the treatment, some mild cases of UTI in men do not require specific treatment or medications, and they can go away on their own.
However, if they reoccur, or if they are severe, these infections need to be treated with antibiotics that will kill the bacteria.
Symptoms and complaints associated with UTI can be relieved using pain killers, like ibuprofen.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...