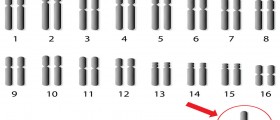
Turner syndrome is a condition which is also referred to as the Ulrich-Turner syndrome or gonadal dysgenesis. This is a condition which solely affects females, manifesting through several conditions, most commonly encompassing monosomy X, where a whole sex chromosome is missing in an individual.
Basically, while normal females have two X chromosomes, in Turner syndrome, one of these chromosomes is missing or abnormal. Sometimes, the chromosome in question may be absent in some cells, while being present in some others nevertheless, leading to a variant of this condition called Turner mosaicism.
If you desire to learn more about this condition, the following lines will provide you with all the basic knowledge you need.
Signs and Symptoms of Turner Syndrome
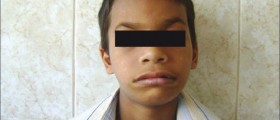
Many different physical and mental impairments are encompassed under the term of Turner syndrome. Namely, the affected individuals are often short, with swellings on their arms and feet, having a broad chest with widely spaced nipples. Additionally, the hairline in these females is expected to be quite low, along with the ears.
Women who suffer from Turner syndrome are not fertile and cannot give birth to children. They have undeveloped gonadal structures which undergo fibrosis in the future. Due to the fertility issues, these women do not have menstrual periods.
Furthermore, these individuals are likely to be obese or overweight with underdeveloped breasts, having a heart-shaped thorax and small fingernails, as well as a facial structure typical for Turner syndrome. Due to the cystic hygroma which affects people with Turner syndrome during childhood, they are likely to have a webbed neck.
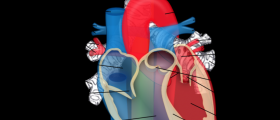
As far as the internal organs are concerned, coarctation of the aorta, bicuspid aortic valve and horseshoe kidneys are common signs of Turner syndrome.
These individuals are prone do developing ear infections and some learning disorders, along with several other behavioral disorders such as ADHD, nonverbal learning disability and memory and concentration issues of other types. These problems are likely to get most prominent during adolescence.
Ultimately, some less common signs which appear hand-in-hand with the Turner syndrome are small lower jaw, inverted elbows, upturned nails, drooping eyelids or pigmented moles, hearing problems and high-arch palate.
However, bear in mind that Turner syndrome affects each female uniquely and some signs and symptoms may be present in a single individual while being absent in another.
Significant Medical Problems Associated with Turner Syndrome
About 15% of all females with Turner syndrome suffer from bicuspid aortic valves, having two aortic valves instead of three, which is the normal biological occurrence in healthy people. Even though the two aortic valves may manage to perform all the functions without problems, they are likely to fail in the long run. Therefore, this condition is usually not detected until some serious symptoms appear. Moreover, this decreased number of valves increases chances of calcification. This is a congenital disorder which is commonly found in people suffering from Turner syndrome.
Additionally, these individuals are likely to have coarctation of the aorta, signifying that the aorta gets more narrower in its lower parts. This health problems affect about 6.9% of people with Turner syndrome. However, according to information provided by Dawson-Falk and others in 1992, this condition is present in up to 12.5% of all Turner syndrome patients. Moreover, females who are suffering from this health issues are usually suspected to have the syndrome too.
A small number of Turner syndrome patients suffer from partial anomalous venous drainage, aortic dilation, dissection and rupture and some other aortic abnormalities. However, aortic root dilation can be present in up to 42% of patients, being one of the common disorders related to this syndrome.
Management Options
Due to the fact that Turner syndrome is a type of chromosomal congenital condition, it cannot be prevented nor cured. Nevertheless, certain steps can be taken to help a person minimize the occurrence of symptoms related to the syndrome.
For example, administering growth hormones or some other hormones helps these patients overcome growth issues and reach normal height. Estrogen replacement therapy is very useful too, allowing Turner syndrome patients to develop sexual characteristics, keep their bones well developed and strong and maintain proper tissue health.
Also, in the modern world of contemporary medicine, women suffering from Turner syndrome can get pregnant if they want to, using a donor egg to create an embryo, being implanted into the woman with this health problem. However, in order for this to be possible, the affected woman needs to undergo estrogen replacement therapy and all other hormonal therapies beforehand.
All in all, statistically, 1 in every 2,500 girls are born with symptoms of Turner syndrome. It is a chromosomal condition which cannot be cured. Fortunately, through early diagnosis and proper treatments, affected girls can grow up to be healthy women, overcoming many of the debilitating symptoms of this condition. Nevertheless, if the syndrome is not managed on time, the consequences can be quite severely impairing.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...