What is Turner Syndrome?
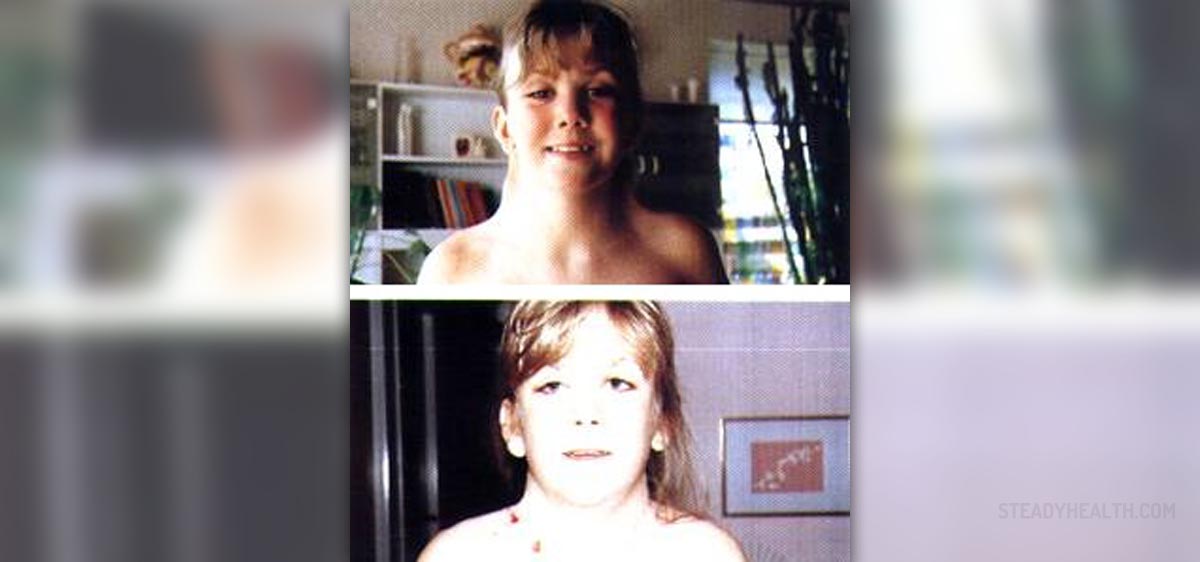
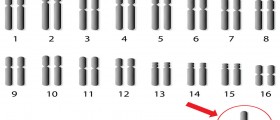
Turner syndrome is a genetic condition, which is most often characterized by the absence of an entire sex chromosome, also known as monosomy. Healthy individuals have 46 chromosomes in total, out of which there are 2 sex chromosomes. Persons affected by Turner syndrome are missing all or a part of a sex chromosome. Also, there are instances in which the chromosome is absent from some cells but present in others which is termed as Turner mosaicism.
As far as the prevalence goes the condition affects anywhere between 1 in 2000 to 5000 phenotypic females, while at the same time being responsible for around 10 percent of miscarriages. In addition, the signs and symptoms include a small neck, ears positioned fairly low, low hairline, broad chest, and shortness. Females with Turner syndrome usually suffer from void ovaries, which in turn results in a lack of the menstrual cycle and infertility. Coupled with Turner’s syndrome there are often other medical problems such as various autoimmune diseases, vision and hearing problems, diabetes, hormonal problems, and congenital heart disease. Aside from physical problems there are often psychological issues present as well. Cognitive impairment such as special, visual, memory, and mathematical difficulties follow individuals affected by Turner syndrome.
The condition is diagnosed by studying the cells, usually taken from the skin or blood. The mosaic Tuner syndrome could in many cases be diagnosed prenatally, before the baby is even born. In addition, in some instances the affected women should definitely have their non working ovaries taken out as they are at an increased risk for developing cancer. As far as the genetic research goes, a gene termed SHOX has been identified as one of the contributors to the condition. Mainly, the lack of one copy of this gene is shown to lead to many of the Turner syndrome symptoms, especially the short stature. Further research is definitely needed in order to provide better treatment options and eventually prevent genetic anomalies as much as possible.
Mosaic Turner Syndrome
As previously mentioned, mosaic type of Turner syndrome is characterized by the absence of the sex chromosome in some cells and its presence in others. The mosaic Turner syndrome is one of the more moderate types of the disorder. Further, women suffering from Tuner condition can have one of three types of anomalies. Firstly, the sex chromosome can be erroneous in all cells. Secondly, there are instances in which the sex chromosome is simply not present in any cell. Lastly, the sex chromosome can be present in some cells but absent from the others. In the case of mosaic Turner syndrome the chromosome could be lost during conception, which explains why it is found in some cells but not in others.
When it comes to the symptoms, as there is a possibility that only a small number of cells are affected, they are relatively tolerable. For instance, a girl may not have any problems with her menstrual period until early adulthood as opposed to not menstruating at all. In addition, diagnosing mosaic Turner syndrome is a fairly simple task, which requires testing of the skin or blood cells. If the results are 45,X (10)/46,XX (90) for instance, in that case the X monosomy is present in 10 percent of the examined cells. Mosaic Tuner syndrome is also the most widespread of all the types of the disorder.
In addition, there are a few subtypes of the mosaic Tuner syndrome, which include ring chromosomes, isochromosomes, and partial deletions. The ring chromosomes are torn at the ends and looped in a form of a ring. The isochromosomes have lost one of their arms which is then replaced with an exact copy of the other arm. Finally, the partial deletion occurs when a segment of the chromosome is absent.
Although the exact cause of the Turner Syndrome is unknown the scientific community is fairly certain that the abnormal development occurs after conception while the embryo consists of anywhere between 2 to 100 cells. On the other hand, it is fairly difficult to express an outcome in advance as far as the severity of the symptoms goes. As is the case with many genetically based disorders every individual affected by them is unique and expresses different symptoms in different ways. Therefore, it is very important to discus all aspects of the disorder and a particular case with a genetic counselor or an endocrinologist in order to better understand the person as well as enable close family and friends to adequately treat and take care of the affected individual.
Finally, when it comes to ovarian problems of women with mosaic Turner syndrome it should be noted that in many cases they have much better functioning ovaries than some of the other persons affected by different types of the condition and can in fact become pregnant.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...