Angelman syndrome is a neurological condition manifesting through an intellectual and developmental impairments, along with sleep problems, sudden, jerky movements and a common happy demeanor, followed by laughing and smiling.
Due to the last couple of symptoms mentioned, this condition was commonly referred to as the happy puppet syndrome. However, due to the stigmatizing effect of this type of a name, the syndrome was later renamed, once a British pediatrician described it in detail in 1965. Since the name of this man was Dr. Harry Angelman, the syndrome received his surname. Today, people suffering from Angelman syndrome are informally called angels, both due to the name of this health problem and the name of the above mentioned doctor.
Neurological Disorder
Even today, it is still unknown how many people in the world suffer from this syndrome, nor how many people are likely to show symptoms of it in the future. Nevertheless, several studies were conducted on school children aging from 6 to 13, living in Sweden and Denmark. This study resulted in AS prevalence of about 1 in every 20,000 in Sweden and 1 child in every 10,000 children in Denmark.
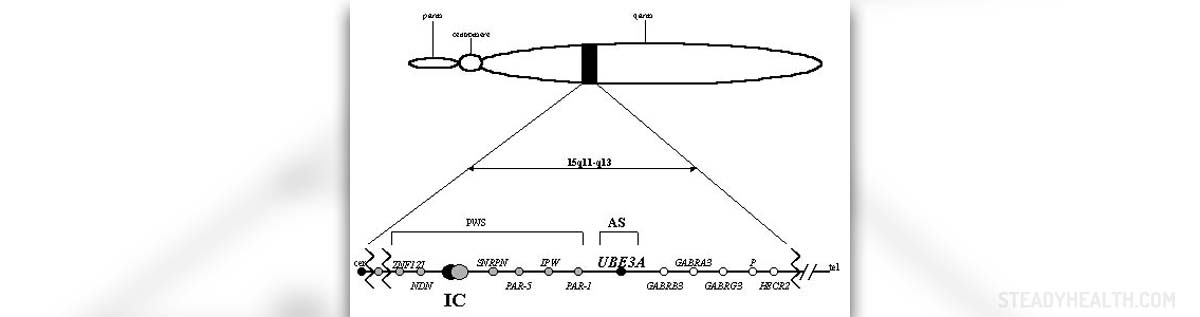
If we are to take the causes of this syndrome into consideration, there are several characteristics of the AS. First of all, from the point of view of pathophysiology, AS occurs once a newborn does not have a mother's contribution on a part of the chromosome 15, commonly with a part of this chromosome missing. However, this is not the only cause behind AS. Rather, uniparental disomy, translocation and gene mutation in this area may lead to AS too.
As for the clinical features of children and people suffering from the Angelman syndrome, this condition usually goes hand-in-hand with severe developmental delay and a severe speech impairment. Also, these people are likely to have problems with their balance or movement. Furthermore, they are bound to express frequent laughing and smiling, appearing very happy and satisfied. AS makes people easily excited, even though they are likely to have a very short attention span, due to their lack of concentration.
By the age of 2, children with AS may start suffering from seizures. Fortunately, the seizures commonly pass before the age of 3. During this period, it is common for children suffering from AS to experience abnormal growth in the head area.
When subjected to EEG scanning, people with AS usually get results which are abnormal, appearing through strange, yet characteristic patterns with large amplitude, slow spike waves.
Frequently, individuals who are born with Angelman syndrome suffer from various other disorders as well. Strabismus, hypopigmentation of the skin and eyes, swallowing and sucking disorders, feeding problems, sleep disorders, water fascination, smooth palms and flat backs of the head are all common health problems and anomalies which appear with the AS.
How is Angelman Syndrome Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of this syndrome takes place through observation of the presence or absence of some or all of the above mentioned symptoms. Usually, the EEG is the main tool of diagnosis, since AS has a very distinct pattern, being much more abnormal that health experts would usually expect. Once a person has all the physical and neurological signs of AS, the EEG confirms the diagnosis.Till this day, there have been no effective treatments or means of prevention for this condition. However, the seizures which accompany it usually need medical assistance. Nevertheless, through various forms of therapies, such as communicational, occupational and behavioral ones, it is possible to help people with AS reach the highest possible state of their mental and physical development.
Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are likely to allow a person with AS to live normal lives, with normal life spans. However, things like clothing without zippers or buttons and some other types of assistance might be necessary.
Usually, these people enter puberty around the same time as everyone else and manage to learn how to eat and dress properly by the time they reach adulthood. Performing simple house tasks can also be expected of people with the Angelman syndrome. However, one should pay close attention to the obesity problems which can be common in women with AS and worsening of scoliosis during adulthood, if this disease is already present in people suffering from this condition. Finally, the affectionate nature, which is quite common for these people, may present an obstacle when it comes to early social life, especially if this trait remains present during adulthood. Fortunately, people with AS can usually be taught out of this behavioral pattern.
All in all, this condition has a set of manifestations and symptoms, making it a characteristic health and behavior problems. The most prominent signs of the Angelman sydrome are severe developmental, speech and intellectual impairment and the prevalence of a happy demeanor, commonly combined with laughter and smiling.
Do not forget that early diagnosis and treatment can improve the lives of people with AS.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...