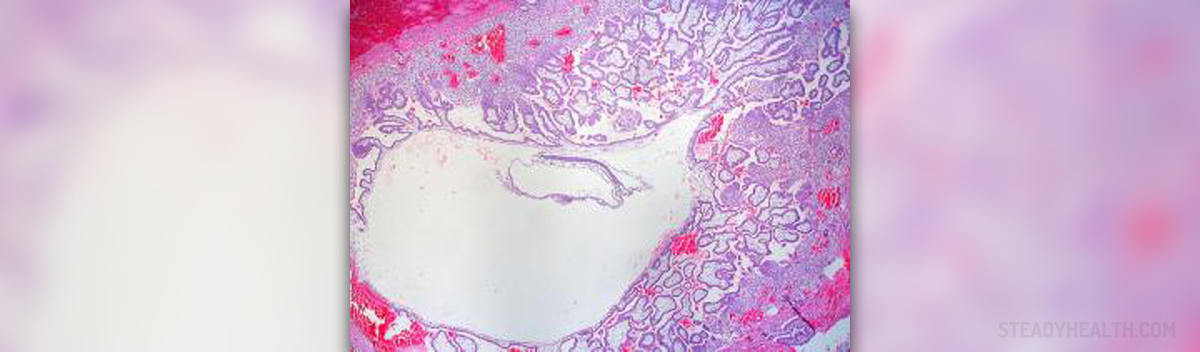
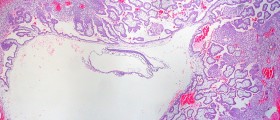
Tubal Pregnancy - Overview
Tubal pregnancy is a serious condition in which fertilized egg is implanted in the fallopian tube. The embryo may grow to certain size and it then causes rupture of the fallopian tube. This may cause serious complications and requires prompt medical care. Tubal pregnancy may be even life-threatening and this is why it is best if it is found prior the rupture of the affected fallopian tube.
In many cases there is no explanation why tubal pregnancy has occurred. On the other hand, certain women are at higher risk of developing tubal pregnancy. They include women suffering from pelvic inflammatory disease, women who have undergone abdominal surgery, those who have had tubal ligation and later tubal ligation reversal. The previously mentioned leads to conclusion that any cause which leads to scarring may affect the fallopian tubes and prevent proper transfer of the fertilized egg and its normal implantation in the uterus. Tubal pregnancy affects older women more and women between the age of 35 and 44 carry the highest risk for this medical condition.
Symptoms of Tubal Pregnancy
Unfortunately, the early symptoms and signs of tubal pregnancy are most commonly omitted. In some women the symptoms are similar to those in normal pregnancy and they initially include absence of periods, positive pregnancy test, breast tenderness and nausea. However, once the embryo has grown enough and led to rupture of the fallopian tube the symptoms include pain and cramping in the pelvis and/or abdomen. The pain is usually located on the one side of the pelvis or lower abdomen. And finally, the woman may experience vaginal bleeding or spotting.
Ruptured fallopian tube is life-threatening medical condition and it requires prompt hospitalization and surgery. The pain is severe and if there is heavy abdominal bleeding a woman may experience lightheadedness and sometimes even lose consciousness. Bleeding causes drop in blood pressure which can be easily measured.
Diagnosing Tubal Pregnancy
The doctors must act urgently since the rupture represents a serious and potentially lethal condition. As soon as the diagnosis has been confirmed the patients are surgically treated.
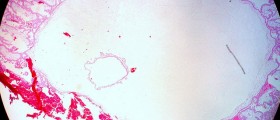
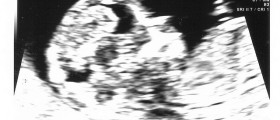
In case, there has been no rupture and the doctor suspects the woman is suffering from tubal pregnancy he/ she performs additional tests including gynecological examination, a blood test which gives perfect insight in whether the pregnancy is in the uterus or in the fallopian tube, pelvic ultrasound which does not show the presence of the embryo inside the uterus. And finally, since in pregnant women progesterone is elevated, if there is no increase in the level of this hormone this may point to the presence of tubal pregnancy.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...