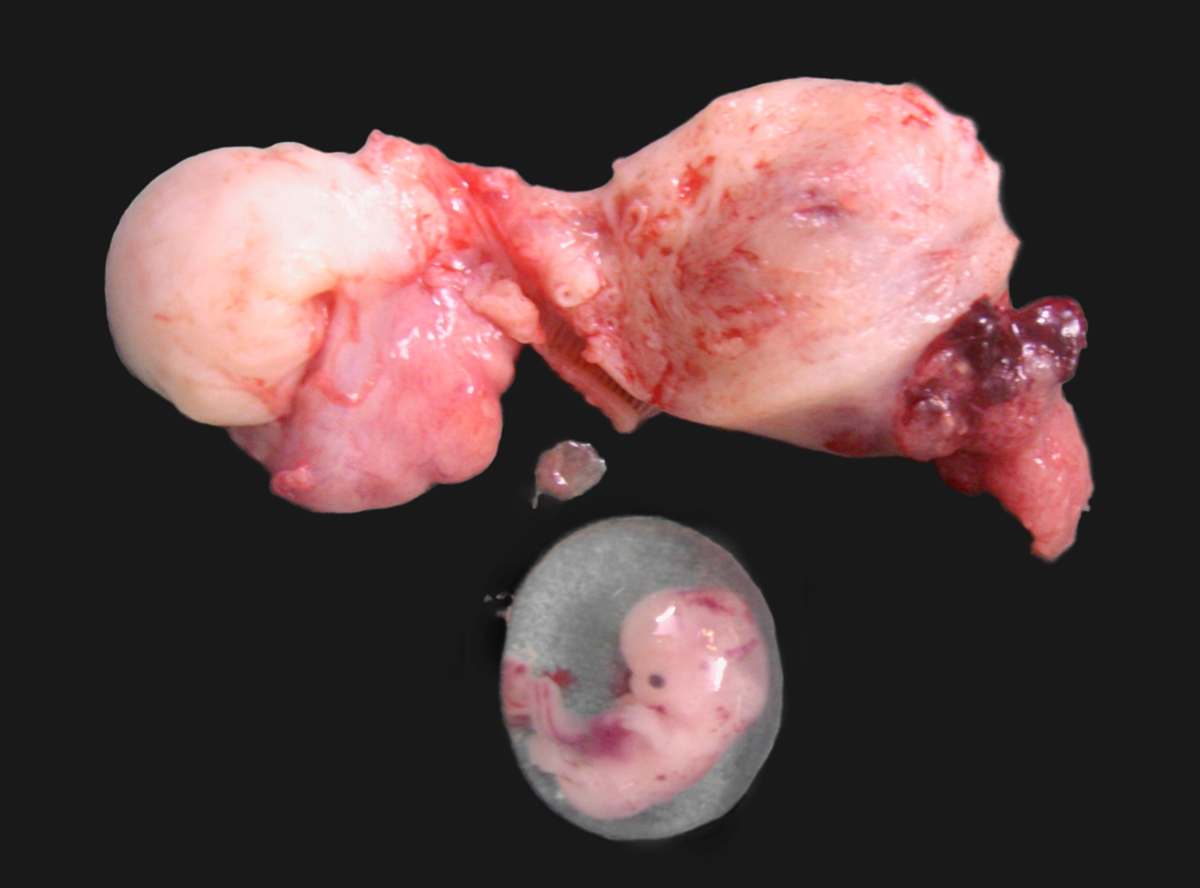
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. This condition represents abnormal pregnancy where fetus cannot neither develop nor survive. In most ectopic pregnancies, fertilized egg settles in the fallopian tubes whilst rarely this abnormal pregnancy may occur in ovaries, abdomen or cervix. Since fallopian tubes do not provide much space for fetus development, as the pregnancy advances the tube starts to stretch resulting in intense pain. This may eventually cause the organ to burst, which may cause severe internal bleeding and threaten life of the mother.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
In normal pregnancy, a mature egg is fertilized inside the fallopian tube and then it moves to the uterus where it attaches to the walls of the organ. In an ectopic pregnancy, a fertilized egg usually remains stuck inside the fallopian tube or implants anywhere outside the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy that occurs inside the fallopian tubes is also known as tubal pregnancy and may be caused by damaged, scarred or distorted tube. The fallopian tube may be blocked or narrowed due to previous tube infections, surgery of fallopian tubes and other causes although sometimes the reason of an ectopic pregnancy is unknown.
Symptoms of Ectopic PregnancyInitially, an ectopic pregnancy is hard to identify because the symptoms are similar to normal pregnancy. However, the first warning symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include lower abdominal pain that may be confined to one side of the abdomen, abnormal vaginal bleeding and cramping on one side of the pelvis. If the fallopian tube ruptures, a woman may experience symptoms such as, severe abdominal and shoulder pain, extreme lightheadedness or fainting, internal hemorrhage and intense pressure in the rectum.
Risks of Ectopic PregnancyRisk factors for ectopic pregnancy are:
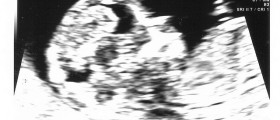
Age over 35 History of tube infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease, Chlamydia and Gonorrhea Previous abdominal surgery Use of an intrauterine contraceptive device Use of fertility medications Previous ectopic pregnancy Smoking In vitro fertilizationDiagnosis and Treatment for Ectopic PregnancyAn ectopic pregnancy can be diagnosed with an internal or transvaginal ultrasound imaging test. Blood tests that measure hormone human Chorionic gonadotropin can confirm the diagnosis. Once diagnosed, an ectopic pregnancy can be treated in two ways. One of the treatments involves surgery to remove affected fallopian tube and it is usually done by laparoscopy. Another treatment includes injection of drug Methotrexate to stop cell growth. In case that fallopian tube has ruptured an emergency surgery must be performed.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...