Information on Thyroxine
All possible thyroxine side effects only depend on the dose that has been given to the patient. Side effects also usually require some time before they start kicking in. Thyroxine is the thyroid hormone T4, and it can also be purchased as a synthetic version. The synthetic version is usually used in hormone replacement therapy for those patients who suffer from numerous different types of thyroid problems.
There are different types of genetic versions of synthetic thyroxine available everywhere around the world. They are of great help to those who suffer from hypothyroidism, enlarged thyroid gland, or goiter.
In some rare cases, it can also be used for the treatment of thyroid cancer and lymphocytic thyroid. There are still some patients who suffer certain side effects of thyroxine which are usually affiliated with overconsumption and inadequate dosage.
Thyroxine Side Effects
Thyroxine can be produced in the human body, but synthetic thyroxine can be used as a replacement, although it sometimes may be associated with certain side effects. Side effects usually do not occur if one follows the individual dosage instructions strictly. Certain types of blood tests are sometimes required for the fine adjustment of thyroxine dosage.
Dosage increase may result in increased metabolic activity and palpitations. There are also numerous other side effects of thyroxine, such as chest pain in those who suffer from numerous different types of heart diseases. Other common side effects of thyroxine may or may not include joint pain, decreased bone mineral density, muscle weakness, severe forms of dyspnea, muscle cramps, insomnia, sweating, irritability, tremors, and anxiety.
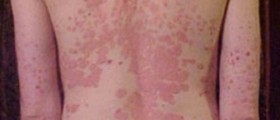
Thyroxine may also be harmful because in some cases it increases the risk of osteoporosis. It can also be affiliated with certain severe types of allergic reactions which commonly include symptoms such as skin rash, itching, and hives. Thyroxine may also cause certain changes in menstrual periods in female patients, which can ultimately lead to irregular menstrual cycles, impaired fertility, and heavy flow.
- Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is defined as a serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level (4.6–10 mlU/L) above the upper limit, despite normal levels of serum free thyroxine. In Pakistan, SCH prevails up to 4.1% in adults, and 5.4% in children and is more inclined towards females.
- Recent studies by Brito et al., show that use of Levothyroxine in nonpregnant adults with SCH (thyrotropin level elevated but ?10 mIU/L and normal free thyroxine [FT4] levels), demonstrate no clinically relevant benefits of levothyroxine replacement for quality of life or thyroid-related symptoms.
- The studies proving this are not limited in numbers, they demonstrate an association between long-term levothyroxine therapy and increased risk of heart disease, osteoporosis, and fractures. In addition to this it also increases the economic burden on the patients owing to price surge.
Among numerous other medical conditions, side effects of thyroxine may also include swelling of the mouth, fatigue, swelling of the face, shortness of breath, swelling of the lips, trouble sleeping, swelling of the tongue, severe headaches, tightness in the chest, unusual weight gain, and unusual weight loss.
Thyroxine may also interact with certain types of medications. It requires some time until it reaches its maximum level of effectiveness, and it may take up to 6 weeks in some cases.



-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...