Yeast infections of the throat are common, especially among babies. Their symptoms are characteristic and easily discernable. Fortunately, today, this condition is cured relatively easily, as long as the infection is not too widely spread or neglected for long.
About throat yeast infections
The term “yeast infection” is used to describe any infection in the human body caused by the fungus called Candida albicans. This fungus is easily contracted, and even though it does not qualify as STD, it can be transmitted through oral sex. It is also often seen in babies who are breast fed, and it affects people with a weakened immune system. Throat yeast infections are also called “thrush”.
Like all fungal infections, throat yeast infections are treated with antibiotics designed to eliminate the fungus. During the treatment, it is very important to follow the instructions and to take the whole course of medications, otherwise there is a great chance that the fungus will come back. Aside from antibiotics, a person suffering from throat yeast infection can use remedies like garlic paste, apple cider vinegar and foods or supplements containing acidophilus bacteria.
A person who has a throat yeast infection is considered contagious, so he or she should be careful not to infect others.
It should be noted that oral thrush in adults can be a sign that there is something wrong with the immune system and should be checked by medical professionals, in order to determine the underlying cause of problems with the immune response.
Symptoms of throat yeast infections
Symptoms of throat yeast infection or oral candidiasis can vary, depending on the person’s immune system and overall health and on the severity of the infection.
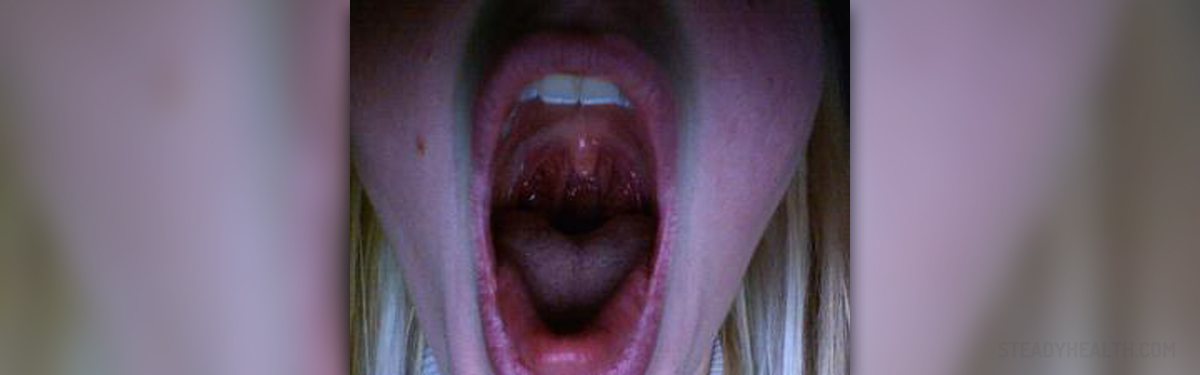
The most prominent symptoms of oral yeast infection are swelling, redness and white spots or patches in the mouth, with general feeling of fatigue, lack of energy, pain, especially while swallowing, and sometimes fever.
The white, lacy patches on top of a red base are the most characteristic and tell-tale sign of oral thrush. They can appear anywhere in the mouth, on top of the tongue, on the roof of the mouth, on gums or on inner cheeks. The patches, which look like milk curd, cannot be easily removed, and if they are wiped off, the lesion may bleed.
Oral yeast infection can also cause the tongue to look red and inflamed, but without the white coating. In any case, this infection causes pain and difficulty eating.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...