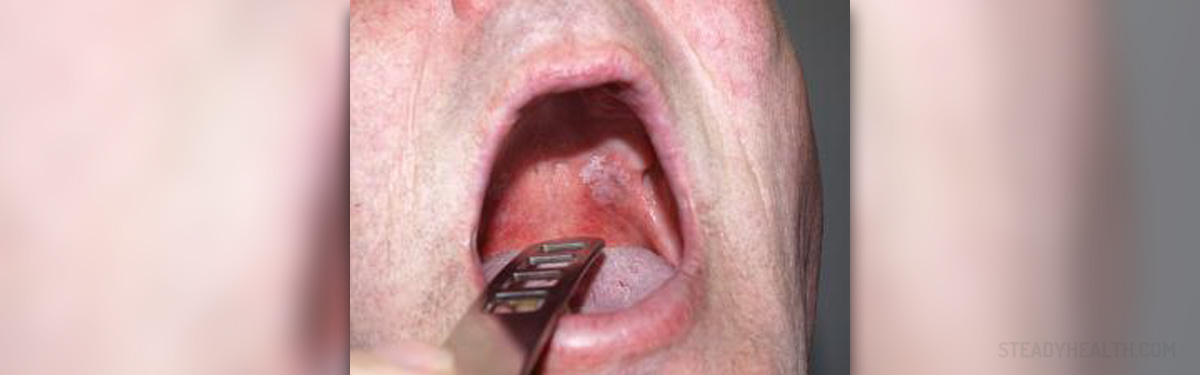
Yeast infection of the mouth is also known as oral yeast infection, or oral thrush. This infection is caused by yeast fungus, Candida, and it affects the mucous membranes of the mouth. Candida infection can occur in other parts of the body as well. It is most common in babies and toddlers, but it generally affects anyone, especially people with a compromised immune system. Persons dealing with cancer or diabetes mellitus may also be at the highest risk of developing oral thrush. Certain drugs, such as Prednisone, or prolonged use of antibiotics, may weaken the immune system and disturb the natural balance of microorganisms in your body, making a person more susceptible to yeast infections of the mouth.
Symptoms of oral yeast infection
For many patients, symptoms of oral yeast infection are not obvious at the early onset of the disease. The symptoms usually develop suddenly and in most adults they include burning sensations in the mouth and throat. A patient will usually become aware of the infection when the creamy-white, slightly raised lesions develop in the mouth. The lesions usually appear on the tongue, on the inner cheeks, on the roof of the mouth, gums and tonsils, or at the back of the throat. These lesions have characteristic “cottage cheese appearance", and they are easily rubbed, scraped, and removed. When the patient removes the lesion, they leave small wounds, which may bleed and hurt. In some of the patients, there is a cottony feeling in the mouth accompanied by a loss of taste. One portion of patients may have cracks at the corners of the mouth. Infants with oral yeast infection may have trouble taking food, or may be extremely irritable. Women whose breasts are infected with Candida usually have red and hypersensitive nipples, pain during nursing or stabbing pain within the breasts.
Treatment of oral yeast infection
A person should seek medical attention whenever the white lesions develop in the mouth. For most of the adult patients, an underlying condition, such as diabetes, will cause oral thrush. If this is the case, the treatment will involve management of the underlying condition. Doctors will recommend eating unsweetened yogurt or taking acidophilus capsules to aid in the treatment of the infection. Yogurt and acidophilus will help restore normal bacterial flora in the body. Immuno-compromised patients will usually take antifungal medications.In infants and toddlers, the infection commonly clears spontaneously, and doesn’t require any kind of medical treatment. For infants and lactating women, doctors usually prescribe a mild antifungal medication and an antifungal cream for mother’s breasts.











_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...