
Urinary incontinence represents loss of bladder control. The problem affects both genders and can be temporary or permanent. In both cases it is rather bothersome and embarrassing. People suffering from urinary incontinence should seek medical help as soon as the problem begins and with adequate treatment the condition may be brought under control.
More about Urinary Incontinence
While some patients complain about leakage of urine only when they cough, sneeze, lift heavy objects or perform similar strenuous activities in others leakage occur spontaneously even at rest.
There are several types of urinary incontinence and stress incontinence, urge incontinence and overflow incontinence are only some of them.
Temporary urinary incontinence may be caused by certain foods and drinks or develops as a side effect of some medications. Overhydration is another potential cause of such urinary incontinence. Inability to hold urine also affects people suffering from urinary tract infections and it is possible to occur together with constipation.
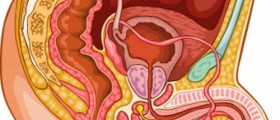
Persistent urinary incontinence is generally a consequence of underlying physical problems and changes. It is, for example, common for pregnant women. The problem becomes permanent in case of some structural damage to the bladder or nearby organs due to complications during childbirth. Furthermore, vaginal delivery always puts pressure to the pelvic muscles due to which a woman may eventually develop urinary incontinence. Persistent urinary incontinence affects elderly people, certain number of women who have undergone hysterectomy, patients suffering from interstitial cystitis, men with prostatitis and enlarged prostate, patients suffering from prostate and bladder cancer and patients with certain neurological disorders.
Therapy for Urinary Incontinence
Treatment for urinary incontinence basically depends on the type of incontinence, severity of patient's symptoms and signs and the actual cause of the incontinence. Many patients undergo a combination of different treatments.
Urinary incontinence can be treated conservatively and surgically. Conservative treatments include bladder training, fluid and diet management, scheduled toilet tips and pelvic floor muscle exercises. Two more conservative approaches are electrical stimulation and radio-frequency therapy. Bladder training and schedules toilet tips are very important and they help patients control urination by holding urine repeatedly for certain period of time or by going to the toilet according to the clock. Foods and drinks that irritate the bladder must be eliminated from one's diet. Pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegel exercises) represent excellent means of strengthening pelvic floor muscles which may eventually reduce incontinence. Similarly, these muscles can be strengthen by electrical stimulation.
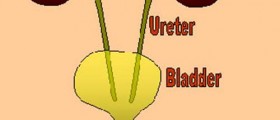
Invasive procedures include injections with botulinum toxin type A, bulking material injections and sacral nerve stimulation. Botulinum toxin injections are beneficial for patients with overactive bladder. Bulking material injections (injections that contain collagen, carbon-coated zirconium beads or coaptite) are applied into tissues that surround the urethra. This way they increase the volume of this tissue, close the urethra and do not allow urine to leak any more. And finally, sacral nerve stimulation includes surgical implantation of a device similar to a pacemaker. The device is implanted under the skin of the buttocks and is connected to a sacral nerve. Electrical current originating from the device stimulates the nerve and controls urination.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...