
Physiology of Both Types of Acne
There are two basic types of acne, inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Non-inflammatory type of acne lesions are not painful and they represent collections of dead cells and oil trapped inside the follicles. Clogging can be caused by comedogenic products and there is also a chance that other environmental factors participate in the clogging process. In this case the follicle either stays open (blackhead) or it is closed (no head or a white head).
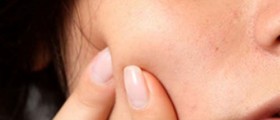
On the other hand, inflammatory acne develop as a consequence of imbalance of androgen and estrogen hormones. Normal pilosebaceous unit comprises a sebaceous gland, a rudimentary hair and a wide follicular canal. The canal is lined with squamous cells. Desquamated cells are carried by sebum and this is eliminated via the skin pores. In case of, for example, an overabundance of male hormones in the area of sebaceous glands or reduction in female hormones the production of sebum increases and this leads to its accumulation inside the follicle. Cell desquamation increases as well. Such accumulation represents an excellent environment for propioni bacterium acne bacteria. Excessive multiplication of bacteria leads to inflammation. Inflammatory acne lesions are always sore and painful.
Anatomy of Non-inflammatory Acne
Non-inflammatory acne range in size from microscopic portions to visible size. A microcomedo represents a small impaction of dead cells, bacteria and fatty acids from sebum and debris in a follicle. They are not visible with the naked eye. Sebaceous fillaments are another form of non-inflammatory acne. They develop around the nose and in oily areas. Comedones, obstructed follicles, are quite visible. Milia is a term for a pearly-white closed comedone that commonly develops around the eyes, nose and on cheeks. This type of comedone requires incisional removal. White heads are closed comedones and finally, there are open comedones also known as blackheads that typically dilate follicle openings.
Anatomy of Inflammatory Acne
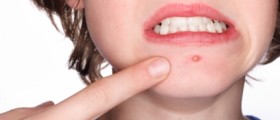
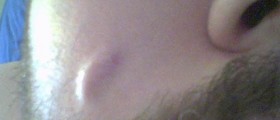
A papule is a red and sore bump made of sebum and debris. There is no pus but the inflamed follicle is still tender to touch. A pustule is a raised and inflamed acne with the presence of pus where the pus is located in the higher portion of the follicle and even reaches above the surface. In this case the infection has actually gone through the entire length of the follicle. A nodule is something like a papule but in this case the inflammation goes much deeper. The skin lesion is solid and very painful. Nodules are simply not extractable and are only treated with medications. A cyst is a closed sac. They represent the most serious form of acne lesions. This is a deep and encapsulated infection that affected the full length of the follicle. A cyst is swollen, hard and painful. The problem related to cysts is that they destroy the surrounding dermal tissue, leave pock marks and lead to scarring.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...