
Lumps and swellings in the testicles are not uncommon and may have many causes. In most cases, testicle lumps are benign, although sometimes these lumps and bumps may indicate testicular cancer. This is why it is always important to seek medical care if you notice such symptoms. According to Cancer Research UK, less than four in every 100 testicular lumps are caused by testicular cancer. A vasectomy can also cause formation of testicle lump.
Types of Testicular Lumps and Swellings
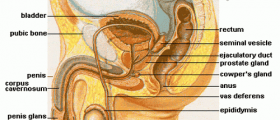
The most common causes of testicular lumps and swellings are varicoceles, hydroceles, epididymal cystand testicular torsion. A varicocele is an accumulation of blood caused by enlarged blood vessels within the testicles. A hydrocele is, meanwhole, a collection of fluid around the testicle. An epididymal cyst is a lump caused by fluid build up in the epididymis, a small tube that helps transport sperm cells. Testicular torsion is a painful swelling caused by twisting of the testicles that cuts off blood supply to the testicles. It is a very painful condition that requires prompt treatment.
Vasectomy: An Overview
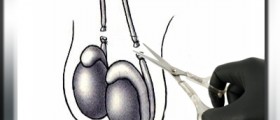
A vasectomy is a type of permanent form of contraception. It is a simple and routine surgical procedure in which the two tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urinary tract are cut or sealed. That way, sperm is still produced but it can no longer mix with the semimal fluid and be carried outside of the body.
A vasectomy is a routine procedure, commonly done on an outpatient basis. It is done under local anesthesia. During the procedure, a doctor makes two small openings in the scrotum to pull out and remove parts of both vas deferens, ducts involved in transporting sperm. The ends of the vas deferens are sealed with small clumps. The procedure takes about half an hour.
After the procedure, a patient may experience pain, swelling and bruising in the operated area. The bruises usually resolve without treatment within two weeks. The patient is advised to wear tight-fitting underwear or jock strap to support the scrotum. Cold compresses are recommended to reduce the pain and swelling. The patient should avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting until full recovery.
Two weeks before and after a vasectomy, medications like Aspirin, ibuprofen, ketoprofen and naproxen should not be used due to the risk of bleeding. For pain management, the patient can take acetaminophen or other over the counter pain relievers, in consultation with their physician.
A vasectomy does not work straight away, and other birth control methods should be initially used because 15 to 20 ejaculations are required for sperm count to be zero.
All in all, a vasectomy is very effective and safe birth control method. It should be done only if you are sure you do not plan to have children in the future. Although, a vasectomy can be reversed, this surgery is difficult and expensive and does not always work.
Vasectomy Complications
Complications of vasectomy are not common but are possible and include bleeding, infection and sperm granuloma. Sperm granuloma is a hard lump in the testicles caused by sperm leakage from the cut vas deferens. This lump is not dangerous but can be painful. Sperm granuloma can be treated with anti-inflammatory medications or surgically removed in case of significant discomfort, but when left untreated, it can indeed cause cysts to form around the area. That is why patients who notice new lumps and bumps after having a vasectomy should always let their doctor know about them, so that any cysts can be treated promptly and other medical conditions can be ruled out.
- www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/testicle-injuries-and-conditions
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/blood-in-semen/
- Photo courtesy of figleaf from realadultsex.com by Flickr: www.flickr.com/photos/figleaf/3098597315/













Your thoughts on this
Loading...