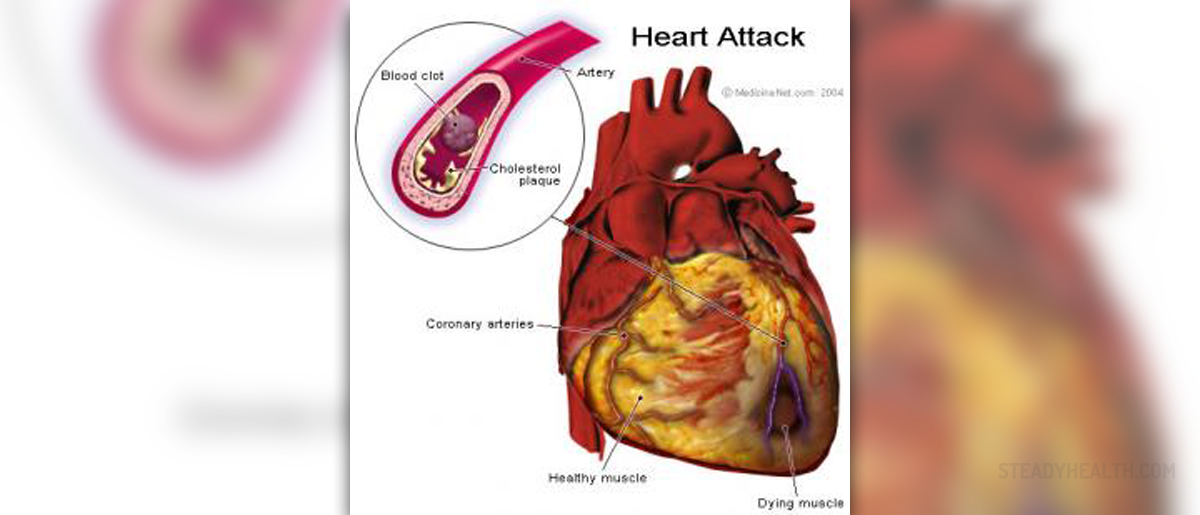
What is a myocardial infarction?
Myocardial infarction is better known outside medical circles as a heart attack. It occurs when the coronary artery becomes blocked and prevents the blood supply to the myocardium. The myocardium does not contain sufficient blood and becomes necrotic quickly, while the fibrous tissue forms in the necrotic area. This reduces the function of the heart chamber that is affected. The prognosis depends on the specific area affected and on how much tissue is damaged. Some cases lead to death, instantly or in several hours, while in others the patient recovers.
What are the symptoms of myocardial infarction?
One of the first symptoms of a heart attack is pain. The pain is severe and is located primarily behind the sternum, which is the breast bone, and it can extend to the jaw, shoulders and arms. The patients usually describes this pain as a tight bend around their chest. The pain can last for several hours and it does not respond to common pain killers.
Shortness of breath, or dyspnoea in medical terminology, occurs either as a result of pain or as a result of pulmonary congestion.
Pallor, even extreme results from the blood that moves away from the skin and directs towards the organs. The skin of patients who are having a heart attack is usually cold and clammy.
Nausea and vomiting may occur because the blood moves away from the gastrointestinal system, adrenaline releases and it may also happen due to the medications administered for this condition.
Patients may experience fatigue which occurs as a result of reduced cardiac output and lowered blood flow to the muscles.
Increased heart rate happens because the heart is trying to compensate for the decreased cardiac output.
Low cardiac output also causes hypotension or low blood pressure.
Tissue necrosis causes increase of metabolites, which leads to high fever. Because of widespread cell death, this condition can last for several days following a heart attack.
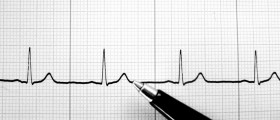
How is myocardial infarction diagnosed?
The diagnosis for a heart attack is primarily done by an ECG. Doctors also checks the cardiac enzymes and the presence of symptoms mentioned above which determine the clinical picture.
A heart attack is not necessarily fatal and the outcome depends on many factors. People who recover from a heart attack are required to make significant changes in their life style, which usually consist of switching to a healthier diet and starting and adequate exercise regimen. These changes are vital as they aim to prevent the risk of a new myocardial infarction.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...