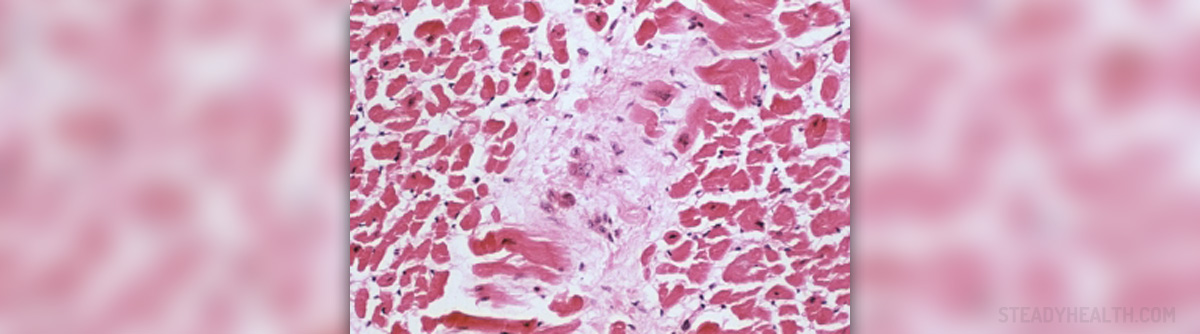
Causes of chronic myocarditis
The inflammation of the heart muscle usually develops as a result of infection by some common viruses such as parvovirus B19, Borrelia burgdorferi (which also causes Lyme disease) or Trypanosoma cruzi. However, it may also result as a hypersensitivity response to drugs or as an autoimmune reaction. For example, if the host is infected by certain species of Streptococcus, the immune system may attack cardiac myosin even when the virus is gone. This happens because Streptococcal M protein has regions (epitopes) that are immunologically similar to cardiac myosin. Worldwide, the most common cause of chronic myocarditis is Chagas' disease, an illness endemic to Central and South America. The condition in which the symptoms of the inflammation of the myocardium persist after an acute infection is known as chronic myocarditis. This condition is characterized by degeneration of muscle tissue and fibrosis or infiltration of interstitial tissues.
Signs and symptoms of chronic myocarditis
Chronic myocarditis is associated with a particular set of symptoms. Most of these symptoms vary in different patients, depending on the level of actual inflammation of the myocardium, or even the sensitivity of heart muscle. If present, signs and symptoms of chronic myocarditis include pain in the region of the chest, which is typically described as strong and stabbing. Patients may also experience congestive heart failure, together with its manifestations: edema, shortness of the breath and hepatic congestion. Patient’s heartbeats may also be irregular. Low-grade fever may also be present, as if the body is suffering some kind of infection. In very young patients, especially toddlers and infants, the symptoms may be non-specific and include general malaise, changes in the appetite, abdominal pain, chronic cough, and respiratory symptoms. In worse cases, sign of chronic myocarditis may even be the sudden death.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...