About Myocardial Infarction
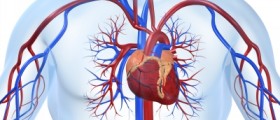
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as heart attack, is a serious and potentially lethal medical conditions that develops due to sudden clogging of heart blood vessels (one of the coronary arteries). This leads to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Since the heart muscle is highly sensitive to lack of oxygen it may soon become necrotic unless the blockage is timely taken care of. Damage to the heart muscle differs and in severe cases large potions of the heart can be damaged which eventually results in lethal outcome.
Myocardial infarction is in majority of cases a consequence of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Build-up plaques narrow the blood vessel and gradually reduce the blood flow. The plaque can also crack and its parts may travel down the blood vessel eventually causing the blockage.
There are many triggers for myocardial infarction. Emotional or physical stress and different illnesses are only some of them. Myocardial infarction predominantly affects people over the age of 65 and is more common in those who are already suffering from other medical conditions (e.g. diabetes, high blood pressure, hypercholesterolemia etc).
The leading symptom of myocardial infarction is chest pain. It is either located to one part of the chest or radiates towards the shoulder, jaw or neck. The pain usually lasts longer than 20 minutes. Additional symptoms of myocardial infarction are shortness of breath, extreme sweating, anxiety, dizziness, nausea and/or vomiting and palpitations.
Therapy for Myocardial Infarction
Patients suffering from myocardial infarction require hospitalization and certain percentage needs to stay in the intensive care unit. In order to confirm the condition doctors use EKG (electrocardiography) and specific blood test (they measure certain enzymes that typically become high due to damage of the heart muscle).
It is essential to open an intravenous line since almost all medications are administered intravenously. Depending on the EKG findings patients may be administered specific anticoagulant. This is a so called thrombolytic therapy. Furthermore, patients are also given oxygen via oxygen mask and drugs that alleviate pain. Since in many cases patients develop serious and potentially life-threatening arrhythmias they require antiarrhythmic medications or electrical cardioversion (defibrillation).
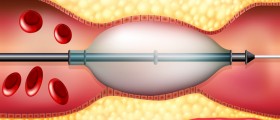
After stabilization patients may be further treated surgically. Angioplasty is a procedure that is supposed to be performed no later that 12 hours after the arrival to the hospital. During angioplasty the surgeon opens the narrowed or blocked blood vessel. After angioplasty the doctor can also perform stenting. This procedure includes placing a small, metal mesh tube called a coronary artery stent inside the affected blood vessel. And finally, emergency coronary bypass surgery is performed in all those patients suffering from severe coronary artery disease of many vessels as well as patients with narrowing of the left main coronary artery.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...