
Myocardial infraction patopsychology is the study of the biological and physical manifestations of diseases as they correlate with the underlying abnormalities and physiological disturbances. Patophysiology explains the processes within the body that result in the signs and symptoms of a disease. Myocardial infarction is a health condition commonly known as heart attack. Heart attack is characterized by the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, which results in a significant damage or even death of the heart muscle tissue. Myocardial infraction is a medical emergency that requires instant professional help. Unfortunately, this condition is often fatal and The World Health Organization estimates that around 12.6 percent of worldwide deaths, each year, were from the heart attack.
Causes of myocardial infarction
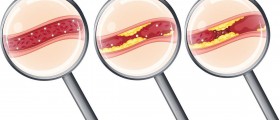
Heart attacks occur when one of the arteries, which supply the heart with oxygenized blood, becomes blocked. Blockage of the arteries usually develops gradually over many years as a result of the buildup of cholesterol. The cholesterol plagues stick to the arterial walls and cause the narrowing of the arteries. The heart attack usually occurs when the cholesterol buildup ruptures forming a clot on the side of the rupture. A clot can be large enough to severely obstruct normal blood flow to the heart. The part of the heart muscle supplied by this artery loses oxygen supply. If the blockage is not quickly undone, the heart muscle becomes severely injured, and the tissue may die. If one of the main coronary arteries is blocked, part of the heart muscle is highly affected. If a smaller branch artery is blocked, a smaller amount of heart muscle is affected.
In rare cases, heart attacks may occur as a result of a spasm of a coronary artery that shuts down the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle. People who use cocaine are at the highest risk of coronary spasms.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
Awareness of heart attack signs and symptoms is very important and may help those people who have a heart attack to survive. The symptoms vary slightly between men and women. Both genders experience common symptoms such as the feeling of pressure in the chest, and pain that is extending beyond the chest to the shoulder, arm, back, or even to the teeth and jaw. The patients feel prolonged pain in the upper abdomen, shortness of breath, sweating, fainting, nausea and vomiting. Women may experience abdominal pain or heartburn, clammy skin, lightheadedness or dizziness and unexplained fatigue.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...