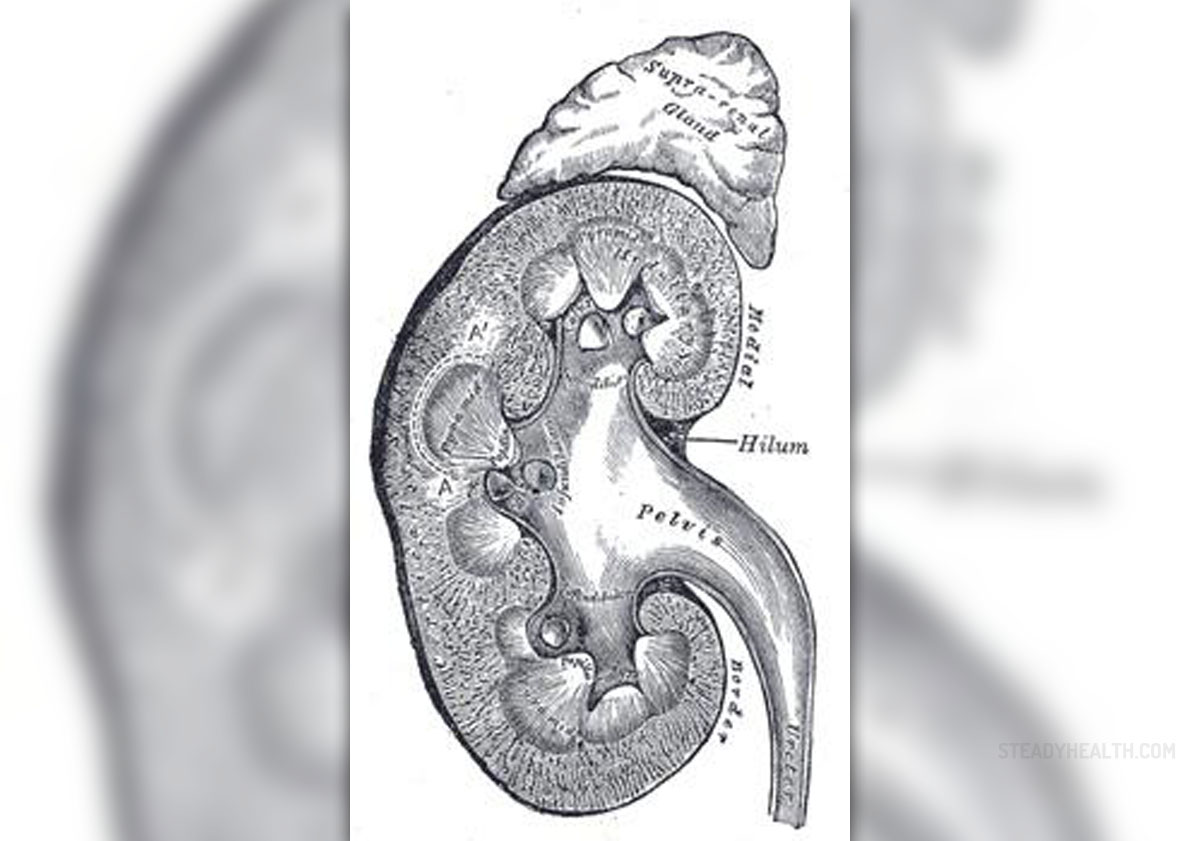
Pyelonephritis is an infection of kidneys. This is an ascending urinary tract infection that starts in the lower portions of the urinary tract and spreads to the pyelum of the kidney. Pyelonephritis can also develop due to bacteria that circulate in the bloodstream. The condition typically features with chills, fever, back pain, nausea and vomiting. In order to set the diagnosis the patients undergo urine analysis as well as several more blood tests. The condition is treated with antibiotics.
What Causes Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis predominantly affects women. The infection is in almost 90% of all cases caused by Escherichia coli, bacteria that is normally found in the large intestine. The risk for pyelonephritis is increased in people suffering from structural abnormalities of the urinary tract, kidney stones, prostate enlargement and those with backflow (reflux) of urine from the bladder into the ureters and into the kidneys. Furthermore, the risk is increased in pregnant women. The condition additionally affect more people who are already suffering from other illnesses such as diabetes as well as those with weakened immune system. Apart from bacteria that most commonly cause pyelonephritis inflammation is in smaller number of cases caused by tuberculosis, fungi and viruses.
Clinical Characteristics of Pyelonephritis
The infection usually starts with fever and chills, pain in the lower part of the back on either side, nausea and vomiting. Approximately one third of patients suffering from pyelonephritis also have symptoms of cystitis including frequent and painful urination and increased urge to urinate. Percussion of the kidneys is painful and sometimes the pain can be so intensive that it leads to spasm of the abdominal muscles.Diagnosing Pyelonephritis
The doctor may assume the patient is suffering from pyelonephritis according to symptoms and sings of the condition. However, he/she performs several more test and exams to confirm the infection. Two commonly performed tests are examining a urine specimen under a microscope and culturing bacteria in a urine specimen to determine the exact bacteria that have led to infection.
Treatment and Prognosis of Pyelonephritis
Patients are prescribed antibiotics as soon as the doctor suspects pyelonephritis and even before samples of urine and blood have been taken for further examination. The choice of antibiotic may be additionally modified according to the laboratory test results. Some patients are prescribed with oral antibiotics and they stay at home while others require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
Majority of patients completely recover from pyelonephritis. Delayed recovery as well as complications develop more in hospitalized patients and in case the infective agent is resistant to commonly used antibiotics. The recovery is also prolonged in people with weakened immune system.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...