What is Prostate
The prostate is male reproductive gland and is responsible for producing the fluid that carries sperm in times during ejaculation. Surrounding urethra, trough which urine passes out of the body, in same cases gland grows bigger, pressing it, and causing bladder and urination problems. This state is called Prostate enlargement or Benign prostatic hyperplasia - BPH, and happens to almost all man in their older age. Half of man will experience prostatitis (infection) of prostate even once in their lifetime.
Based on the severity of your symptoms, various treatments can be recommended, from lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, even surgery.
Types of Prostate Surgery
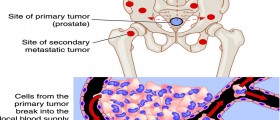
In case of surgery, procedure is called Radical prostatectomy. This procedure is usually used in cancer cases, when cancer is not spread outside of prostate (stages I and II), and it is in early stage. There ate typically two types of performing this surgery; laparoscopic surgery and open surgery.
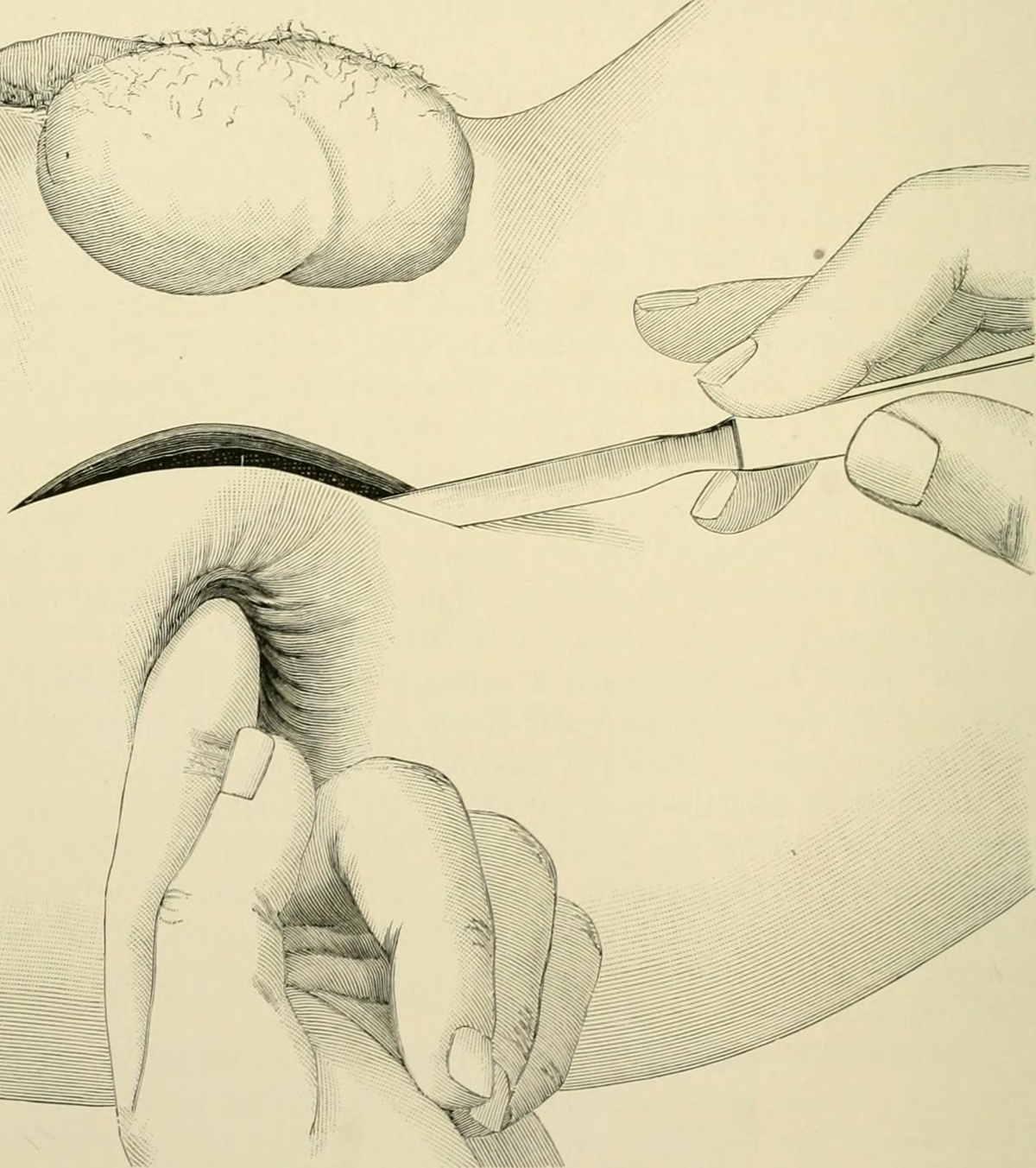
In case of laparoscopic surgery, an instrument called a laparoscope in inserted through small incision in the belly. Then surgeon removes your prostate through incision. This procedure is relatively new, and patient better respond to it, because of less blood loss, and recover faster. This procedure is still relatively new, and it can be also performed by robotic-assisted laparoscope. Goal of this type of radical prostatectomy is to remove all of prostate, and is it used especially in cases of cancer or just the parts of tissue affected by cancer.
In case of open surgery, surgeon also makes incisions, either on groin between the scrotum and anus, or on lower belly. He than removes the prostate, together with the parts of lymph nodes, which are used latter to test for cancer 1.
Radical prostatectomy is usually requires general anesthesia, and 2-4 days hospital recovery time. You will be need catheter (flexible tube that is inserted in your bladder), for 1-3 weeks, together with instructions about post operative care and annual check up with your doctor, especially in cases of cancer. This may include:-digital rectal exams-biopsies, in cases of something is suspected on the tissue-physical exams-specifics set of tests (like PSA – prostate-specific antigen test), to determine speed of PSA level changes, etc.
If detected on time, radical prostatectomy lowers the risk of cancer spreading or growing. You can expect a years of normal life in that case, after successful surgery.
Problems and Complications Post-Op
There are some post-operative problems and possible complications, which you may experience after the prostatectomy procedure. These complications may include:
- some level of damage to the rectum,
- damage to the urethra,
- urinary incontinence (up to 50% of men in post-operative period of 1 year, experience to some degree, problems with urinary incontinence, from occasional dribbling to urinary pads),
- erection problems (up to 80% of men in post-operative period, depending of their age – older men over 60 years – while younger men can restore their ability to have erections).
As prostate cancer is increasingly diagnosed at early stages and technical refinements regarding laparoscopic radical prostatectomy are developed, longer survival outcomes are accomplished. Localized prostate cancer is potentially curable with the appropriate surgical technique. However, postoperative complications, leading to dysfunction of the urogenital system, may last for a lifetime.
- Urinary incontinence occurs in 5–74% depending on the surgical technique, the operative experience of the urologist, the definition of urinary incontinence, and the method of evaluation. It usually appears immediately after the operation but continence recovers partially or fully during the first months. Unfortunately, urinary incontinence will be a lifetime problem for some patients. The symptoms range from post-void dribbling to total loss of bladder control and may appear rarely or occasionally. Urinary dysfunction influences the patient’s daily life, social relationships, sleep and of course self-respect.
- Reports on sexual function in men after radical prostatectomy show large variability with regard to potency. Until the introduction of nerve-sparing concepts, almost all men showed no regain of sexual function after surgery. But even when the anatomical integrity of the nerves seems to have been preserved, various categories of factors have been demonstrated to affect the recovery of potency. Comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, arterial insufficiency or even the patient’s age itself negatively influence erectile function. The recovery of sexual function more likely depends on the surgeon than on the treatment approach (retropubic, laparoscopic or perineal technique).
- Bowel dysfunction may occur after radical prostatectomy and it is marked by fecal incontinence. Fecal incontinence occurs due to the loss of control of the anal sphincter. Consequently, these patients are unable to control the release of colon content. This inability dramatically influences self-confidence, and social life. Age is a significant predisposing factor for fecal incontinence. In elderly people, fecal incontinence happens in up to 4%. Continence of stool is the result of a complex mechanism which includes the integrity of the anal sphincter and the rectum, and it is influenced by stool volume and consistency. During an operation in the region of these anatomical structures, injury may occur, leading to various degrees of fecal incontinence.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...