
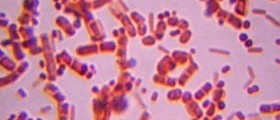
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the bacteria normally foundin the nose and on the skin of many people and animals. Some types of bacteriumhave the ability to produce several different toxins, responsible for foodpoisoning. A person can get infected by eating the food contaminated with Staphylococcusaureus toxins, either by contaminated milk and dairy products or by contact withinfected people working with these foods.
The food which can easily be contaminated with this bacteriumis one prepared by hand, especially pastries, sandwiches, pudding or slicedmeat. However, Staphylococcus aureus is known to grow even in salted meat and bacterialtoxins can’t be destroyed by cooking the contaminated food.
Food Poisoning Symptoms
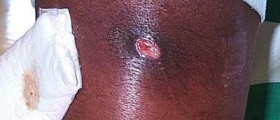
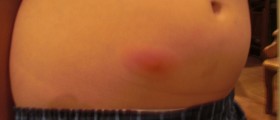
People infected with Staphylococcus aureus toxins usually experiencefirst symptoms very quickly after eating contaminated food. It usually takes 1to 6 hours after the meal until the person start experiencing: stomach cramps,nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Most cases of food poisoning don’t require anytreatment and resolve on their own, after a day or two, but some people might behaving severe problems due to the Staphylococcus food poisoning. Patients mayhave problems with severe fluid and electrolyte deficiencies, due to thevomiting and/or diarrhea, leading to the weakness and shock (hypotension). Children,elderly and people affected by some chronic illnesses are found more likely tohave serious problems with this food poisoning. The condition might be sosevere to cause lethal consequences.
You shouldn’t worry if someone around you is sick from thistype of poisoning, since the toxins can’t harm you and the condition is notcontagious.
How to Prevent and Treat
The most important thing is to prevent the contamination offood with Staphylococcus aureus, even before the bacterium start to produceharmful toxins. Avoid preparing the food if you have any eye, nose or skin infectionsor skin wounds. Always wash your hands before handling the food. Your kitchenand dining room should always be sanitized and clean.
The treatment includes resting and plenty of fluids in caseswhere the bacteria don’t cause any serious problems. Your doctor may alsoprescribe you some medications (injections or suppositories) in order to calmyour stomach, and control vomiting or nauseous feeling. Severe cases might betreated in the hospital with some intravenous therapy, especially if thepatients are children or elderly. The loss of fluids because of the vomitingand diarrhea is most commonly compensated by intravenous fluids. Antibiotics don’twork against this bacterium, because they don’t affect the Staphylococcus toxins.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...