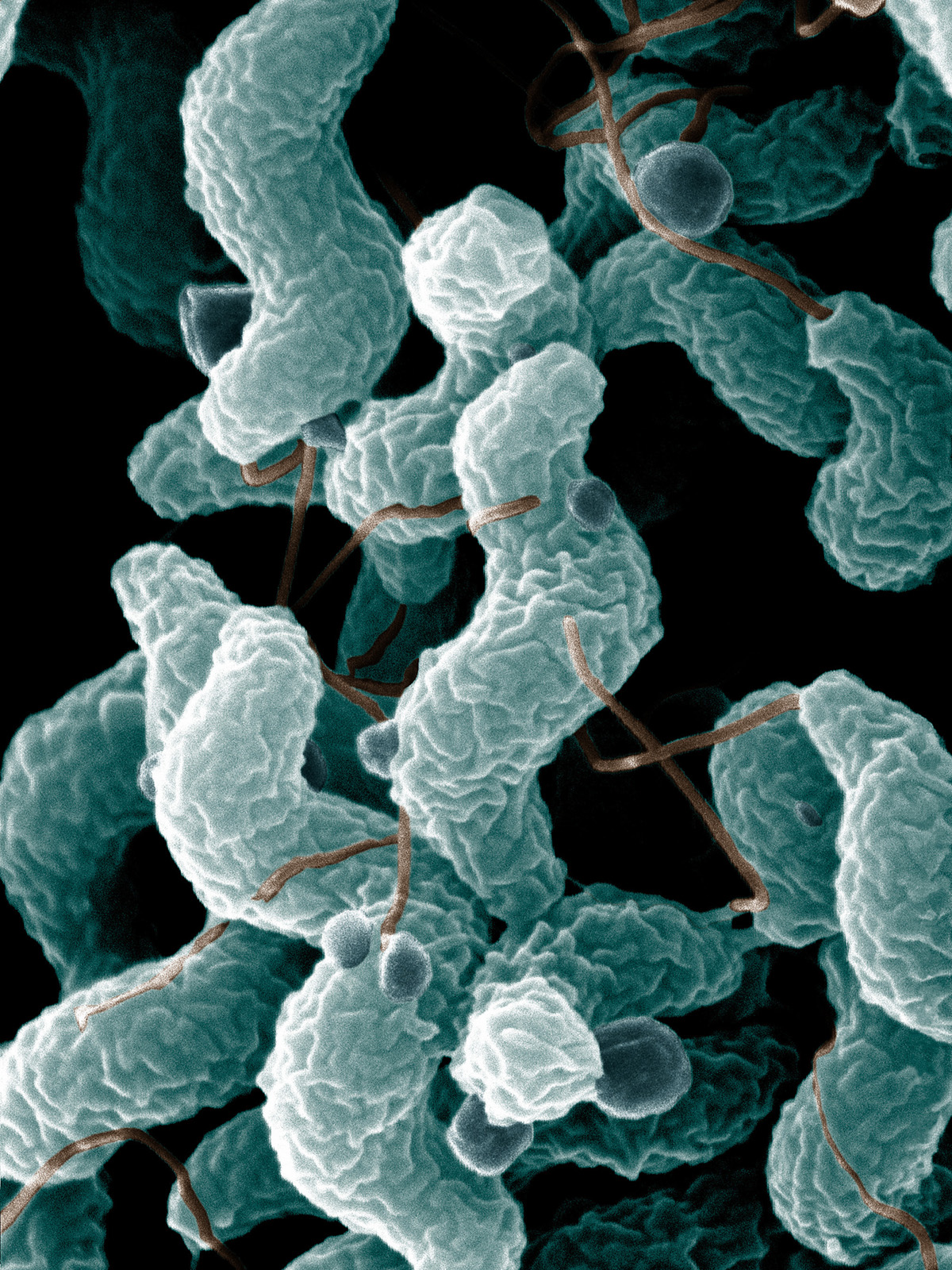
Campylobacter is a gram-negative genus of bacteria that have a characteristic spiral appearance and are oxidase-positive. The name “campylobacter” actually means “twisted bacteria”. Campylobacter jejuni is recognized as one of the main causes of bacterial food-borne disease in developed countries, ahead of Salmonella.
These bacterium was first recognized as a cause of human gastrointestinal illness in 1975. Campylobacter is a termophilic rod that grows best at 42°C (107°F) and low oxygen concentrations. This bacterium grows usually in the intestines of warm-blooded birds and mammals. It is estimated that each year campylobacter causes 2 million illnesses, 13.000 hospitalizations, and over 100 deaths in the United States.
Sources of campylobacter food poisoning
Campylobacter food poisoning results usually from eating contaminated foods. However, in more of 50 percent of cases, doctors are not sure what exactly causes the infection. Food can become contaminated in the process of butchering or animal slaughter. Another way to contaminate the food is when edible portions come in contact with animal feces.
This bacteria can be found in intestines of cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens, ducks, geese, wild birds, dogs, cats, rodents, and marine mammals. Other identified food sources of infection include unpasteurized milk, undercooked meats such as beef, pork, lamb, livestock offal, and occasionally shellfish, fresh produce, and eggs. Pets, such as cats and dogs, can also carry this bacterium in their feces and people, especially children, can get the infection if they get in contact with the feces and forget to wash their hands before touching the mouth.
Signs and symptoms of campylobacter food poisoning
Campylobacter is responsible for a zootomic infectious disease, Campylobacteriosis, characterized by diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, fever, nausea, and vomiting. Patients usually recover after ten days but in some rare cases, the infection may result in more severe health problems. Infections with campylobacter are associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome, a severe health condition that may even result in permanent paralysis. Although rare, it is the most common cause of acute generalized paralysis in the Western world. An extra chronic condition that may be associated with Campylobacter infection is arthritis called Reiter’s syndrome.
Treatment for campylobacter food poisoning
Normally, patients with campylobacter food poisoning do not require any kind of special treatment. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids and prevent the dehydration caused by diarrhea and vomiting.
Anti-diarrheal medications may be prescribed to relieve the symptoms. Antibiotic treatment may also shorten the course of disease. In more severe cases hospitalization will be required and doctors will prescribe antibiotic treatment even before the culture results are known.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...