Bacterial food poisoning
The diarrhea is the most common of all food born diseases. The causes of these diseases might be: bacteria, fungi, parasites, but also different chemicals and heavy metals.
In 90% of the cases food poisoning was caused by bacteria, usually Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter, Clostridium perfringens, certain types of Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella.
You could catch bacteria from the food by eating raw products or even cooked meals, if they were made in unsanitary conditions, without the proper storage and cleaning of the food, or left undercooked.
In order to control the disease it is important to:
Control the present bacteriaPrevent the bacteria growthDestroy bacteriaAvoid re-infectionBacteria Characteristics
Bacillus cereus can be found in rice, potato and macaroni and sometimes in raw food.
Campylobacter jejuni is transferred through the contaminated food and water, usually in the developing countries. Properly cooked and stored food is safe from campylobacter contamination.
Clostridium botulinum is quite rare. It is the disease that comes from canned food. Throw away any can that looks damaged or smell different than it normally does, to avoid the botulin infection.
Clostridium perfrigens is common to the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals and also found in the dust and soil. The bacteria may survive the temperatures between 40 and 140 degrees F, so when freezing the meat, use small portions to cool quickly and prevent the growth of C.prefrigens.
Enteropathogenic type of Escherichia coli is frequently causing diarrhea in developing countries and among the travelers. The condition is also known as the travelers’ diarrhea. Avoid the water and the food that weren’t adequately washed, disinfected and/or cooked, and you shouldn’t worry about this problem.
Listeria monocytogenes is the bacterium affecting the immunocompromised people (HIV/AIDS and some other patients), older patients and pregnant women. Symptoms can vary from mild, fever-like to carrier state and even death, although rarely, in adults. It can survive under extreme circumstances and cause listeriosis.
Salmonella is usually found in the meat, fish and eggs, but any food might be contaminated with this bacterium. Cooking over 150 degrees F destroys the bacteria and refrigeration under 40degrees F controls the bacterial growth.
Staphylococcus aureus often cause infections of the respiratory tract, skin and wounds. In the food, this bacterium produces a toxin, which is responsible for the food poisoning. Bacterium may be damaged by cooking, but released toxin remains active even in cooked food. To avoid contamination with S.aureus, keep the food refrigerated and maintain good personal hygiene.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is sometimes found in the seafood. If properly stored and cooked seafood is safe to eat. The raw seafood causes problems, because it may contain this bacterium.
Yersinia enterocolitica is rarely a cause of the bacterial infection, but the disease can be severe, especially, in children. It may cause intestinal problems, pseudoappendicits, and sometimes arthritis and even death.









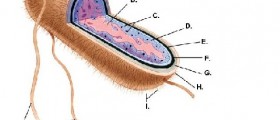






Your thoughts on this
Loading...