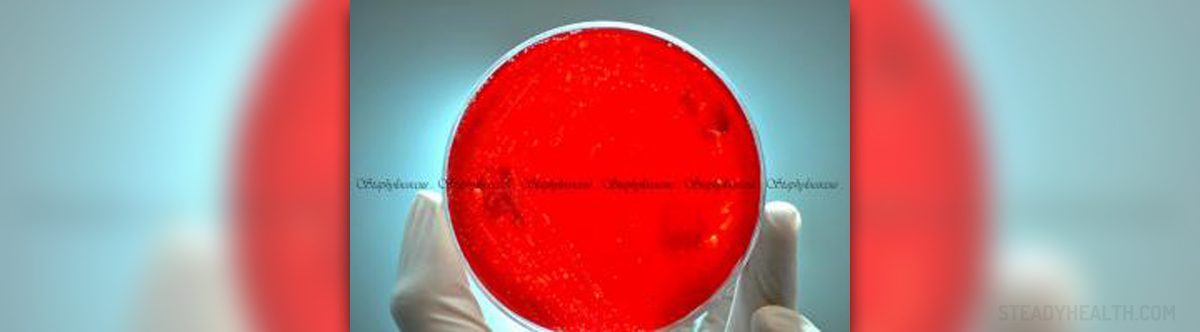
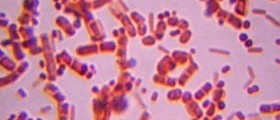
Staphylococcus is a species of Gram-positive bacteria that appears round in shape and form in grape-like clusters. Gram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining, of the high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall.
Staphylococcus genus
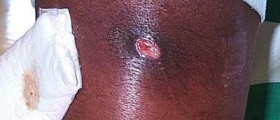
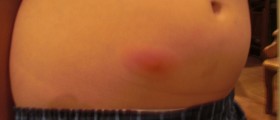
The Staphylococcus genus includes thirty-two species and eight sub-species of which the great majority is harmless to humans and other organisms. It is a widespread bacteria normally hosted on human’s skin and tissues. The most prominent strain of Staphylococcus bacteria is Staphylococcus aureus, which is responsible for staph infections. This bacterium most commonly resides in nose, on armpits and buttocks. Normally it does not show any symptoms but if it gets to the blood stream, it may be extremely dangerous and even fatal, causing severe problems like toxic shock syndrome. In mild cases of infection, Staphylococcus bacteria can cause boils, skin infections, abscesses, and ulcerations.
Infection
Staphylococcus aureus, the most common cause of staph infections is frequently found on the human bodies. It is estimated that approximately 20% of humans carry this bacteria in a long term. Carriers pass bacteria to other people in the casual contact. Sometimes the bacterium is spread in the contact with contaminated surfaces such as handles, beddings, countertops and taps. This bacterium may also colonize food that is not thermally processed. Staphylococcus bacterium is a major problem in hospitals where it is very hard to control spreading of the antibiotic-resistant strains. Patients with compromised immunity and open wounds are at very high risk of developing staph infection, and a great portion of hospital staff are carriers of the virus.
Diagnosis and treatment
A clinical diagnosis is established by laboratory biochemical or enzyme-based tests. In the cases of skin infections, it is diagnosed by the appearance without the need for laboratory testing. Infection of the bloodstream, pneumonia, and endocarditis require culturing of samples of blood or infected fluids. Special tests are needed to determine which antibiotics are effective against the bacteria.
Trivial skin infections are treated topically, with antibiotic ointment. In some cases, doctors may prescribe oral antibiotics. If the infection progress to the second stage, it usually develops into abscesses that are usually surgically drained. Severe staph infections require intravenous antibiotic treatment and the specific antibiotic is determined by culture results in the laboratory. However, Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to most of the antibiotics like methicillin and other antibiotics in the same class, as well as penicillin, amoxicillin, and oxacillin. If left untreated, this infection, known as MRSA, may grow to life-threatening blood or bone infections.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...