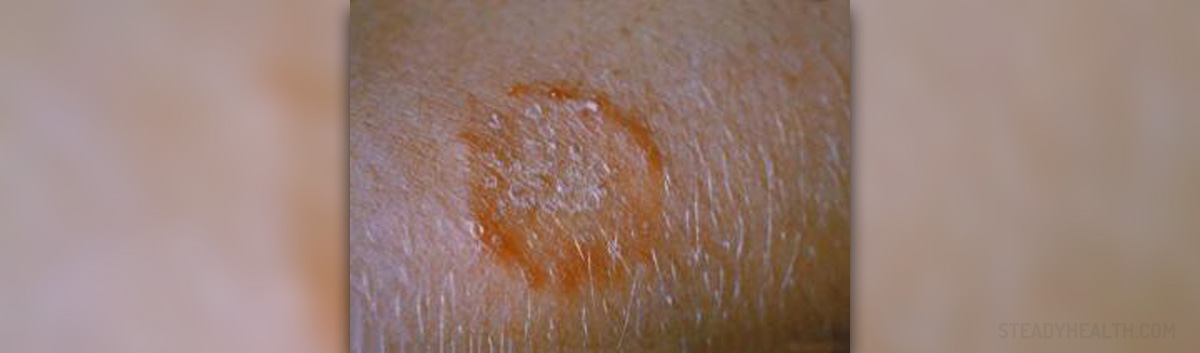
Ringworm, a fungal skin infection, is condition that affects different parts of the body including the skin of the body (Tinea corporis), scalp (Tinea capitis), beard area (Tinea barbae), groins (Tinea cruris) or feet (Tinea pedis).
What are Causes and Risk Factors of Ringworm?
This is a common fungal skin infection and even though it can affect people of all ages it is most frequent among children. The infection develops as a consequence of uncontrollable multiplication of the particular type of fungus.
Ringworm is contagious and can be easily passed by direct contact. Transmission is also possible via contaminated items such as combs, shower/ pool surfaces and unwashed clothes. It is even possible to develop ringworm after contact with the infected animal (usually pets).
Fungus responsible for ringworm intensively multiplies in warm and moist areas. The infection always affects superficial layers of the skin and the fungi never penetrate deeper in the skin or underlying tissues.
Symptoms and Signs of Ringworm
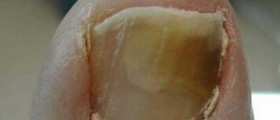
The infection typically features with patches that form on the affected part of the body. These patches are round/ oval and in a form of raised pink and scaly rings. In the very center of the ring the skin is clean and of normal appearance. These skin changes are itchy and by scratching there is a chance for the infection to be spread to other parts of the body. In case of ringworm of the beard and the scalp patients develop bald patches. If nails are infected there is noticeable discoloration, thickening and crumbling.
Diagnosing Ringworm
Diagnosis of ringworm can be set due to the very appearance of the skin lesions. Furthermore, doctors may use a blue light to examine the affected skin. The fungi become florescent once they are exposed to such light (light originating from Wood's lamp). Scrapped samples of the skin are investigated under the microscope.
Treatment for Ringworm
The first thing an infected person must do is keep the affected skin clean and dry. Self-care is generally effective in elimination of the infection. The condition does not linger more than a few weeks. The infected areas are treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications in a form of powders, lotions or creams. They contain different active ingredients such as miconazole, clotrimazole etc.
If the infection becomes recurrent or does not respond to such medications the person is due to consult his/ her heath care provider. He/ she may be prescribed more potent antifungal medications such as ketoconazole. Complications such as secondary bacterial infection of the skin require additional treatment.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...