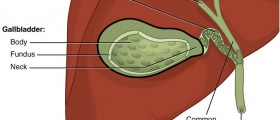
The gallbladder is a tiny organ which is placed beneath the liver. It keeps the bile, a fluid made by the liver, and helps in digestion. This fluid is made of cholesterol, salts and unusable or unwanted substances. When waste products are disproportionate, gallstones may be built. Gallbladder surgery is one of the most regularly performed operations in the United States. This surgical performance is also called cholecystectomy.
Gallstones can make you feel sick. They may cause a high temperature with abdominal pain. This particularly happens after a fatty meal. In order to make diagnosis, a GP may push slightly with his or her fingers just below the ribs on the right side of the patient’s chest. This area may feel tender. Other tests consist of ultrasound scan and HIDA scan (X- ray images).
There are two surgical options: a traditional open cholecystectomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In traditional open cholecystectomy, a surgeon makes a cut which is 4 to 7 inches long, in order to get rid of the gallbladder. This is a very complicated procedure. It is very painful, and it will take a long time for the patient to recover. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is also a common procedure. A surgeon will not have to make large incision. The operation is done with general anesthesia. During this procedure, the surgeon will drag in a laparoscope (a long, thin telescope with a light and camera lens at the top) into the abdomen. It will allow him to see the internal organs on the monitor. The operation takes 60 to 90 minutes.
After the operation, the patient is transported to a recovery room where he is continually monitored. The patient usually does not stay in the hospital more than a day or two. After this surgery, the patient may feel pain in his shoulders and belly. Widespread muscle aches may occur, too.
Food aversion and some nausea are not uncommon. A frequent problem during gallbladder removal recovery may also be gas pain. Diarrhea occurs in about 10% of patients. It occurs as a consequence of the change in the way bile is distributed to the intestine once the gallbladder has been extracted. Removing the gallbladder hastens the passage of food and it may cause the diarrhea. The doctor may prescribe medications which will control the availability of bile salts. The patient may also get painkillers. The return to usual activities is expected after a week, but some people will need to rest for a longer time.
Gallbladder disease is a very common illness, which may be prevented by diet which is high in fiber and low in fat. Drinking lots of water and keeping from caffeine helps as well.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...