
The natural habitat of rattlesnakes is in North and South America. They are rather abundant and this explains the high incidence of rattlesnake bites in these regions. It is estimated that in the Unites States 8000 cases of snake bites occur each year and 75% of all bites are rattlesnake bites. Fortunately the number of deaths caused by rattlesnake bites is small. However, the bite is very painful and can sometimes cause irreversible damage to certain tissues.
There are 30 species of rattlesnakes in the Americas. People who like spending their time in wilderness are at higher risk of encountering this venomous snake and are at potential risk to be bitten.
Symptoms of Rattlesnake Bite
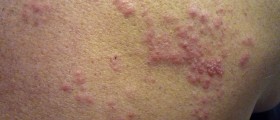
The person will most definitely be aware if he/ she has been bitten. The marks on the skin left by the rattlesnake fangs are quite noticeable and the moment a person has been bitten sharp pain occurs. The bitten part of the skin will become discoloration and have slight swelling. If the bite has been severe the wound may also bleed. The effects of the poison will soon start to appear. The person may experience breathing difficulties, drop in blood pressure, nausea and vomiting. Furthermore, the eyelids can be droopy and one may suffer from blurred vision. The affected area is numb and there may be tingling sensation. Once the blood pressure becomes too low the heart rate rapidly increases. Additional symptoms include thirst, tiredness and muscle weakness.
What are the Effects of Rattlesnake Bite?
Majority of rattlesnakes produce hemotoxic venom. When the venom is injected it starts damaging the tissues and may cause significant imbalance in the circulatory system. The effects of the venom are in a form of internal hemorrhage. What is more, rattlesnake venom contains neurotoxin elements which may cause damage to the nervous system. Even the respiratory system can be affected and there are also cases of lethal outcome. The venom of young rattlesnakes is much more potent comparing to older snakes.
Treatment and First Aid for Rattlesnake Bite
The only effective means against rattlesnake venom is anti-venom which needs to be administered as soon as possible. Still since anti-venom is only available in medical centers the person who has been bitten must know how to react in case he/ she has been bitten.
It is essential to stay calm. Any additional anxiety and exertion may stimulate circulation and contribute to faster spread of the venom. The bitten part of the body is supposed to be held lower than the level of the heart. Any jewelry must be removed as it may hinder the blood flow. Even though the casualty may experience a burning sensation at the site of the bite ice is never supposed to be used in the particular area. One effective way to restrict the flow of the venom is to tie a compression bandage but it must not be tied too tight as it may cause cutting off the blood flow. The casualty must be transferred to the nearest medical center as soon as possible in order to be properly treated and administered anti-venom.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...