About Progesterone
It is a female steroid hormone that a woman’s body produces during pregnancy, menstruation, and embryogenesis. Synthetic progesterone is of a similar chemical structure as the naturally secreted one.
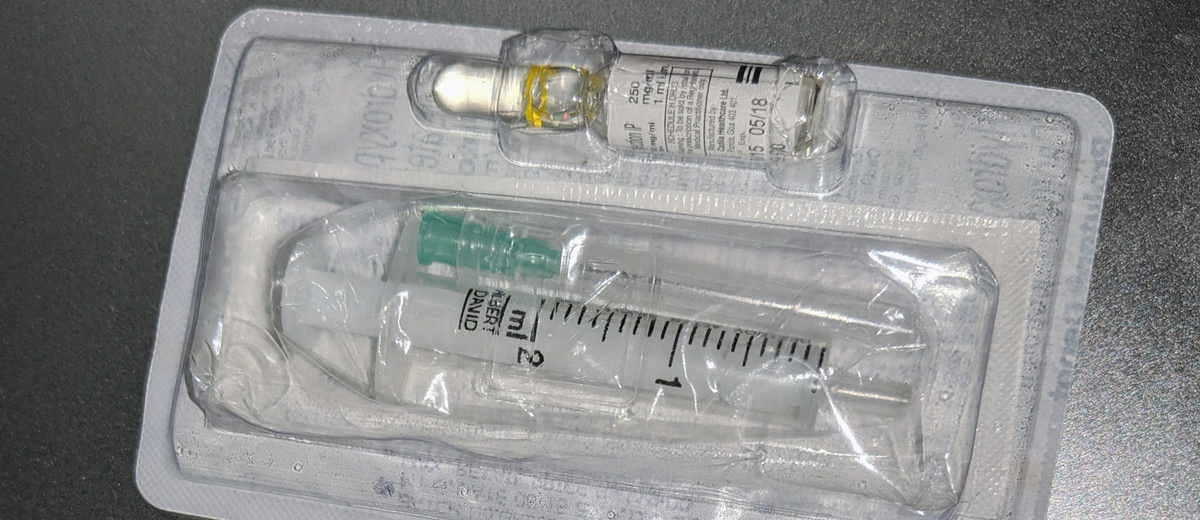
Why Progesterone Shots are Injected
Progesterone shots are administered into the body to compensate for the lack of natural ones. The role of progesterone is to stabilize the lining of the uterus, which directly leads to controlled menstrual bleeding. When progesterone level is increased in the body, the effect is opposite to the prior.
In the case of IVF pregnancy, progesterone is administered for 10 to 12 weeks from the beginning of pregnancy to achieve pregnancy and support fetus development. Unless the level of progesterone during pregnancy is not as it is supposed to be, the walls of the uterus can shed resulting in miscarriage and premature labor. Progesterone shots are also used in the treatment of infertility, and they need to be given by a professional such as a doctor who is educated to do that.
- A retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes from first frozen thaw ET cycles performed between January 2018 and February 2021 was carried out in 580 women attending a large UK centre.
- The endometrium was prepared using (modified) natural cycle or a hormonally substituted cycle, commencing vaginal micronized progesterone for 5 days before ET. Serum P was measured on the day of blastocyst transfer by immunoassay. If this level was
- To assess the efficacy of P supplementation in this ‘real life’ clinical context, the primary outcome of clinical pregnancy rate (CPR) was compared between those with P level on day of ET 50nmol/L. Secondary outcomes included ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) and miscarriage rate (MR).
- Fisher’s Exact Test and Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test for categorical variables and non-parametric regression and Wilcoxon test for continuous variables were applied. ANCOVAs and multiple logistic regression analyses were performed to test hypotheses while controlling for confounders.
- The study cohort had a mean age of 39, mean P of 67nmol/L, mean BMI of 25.1kg/m2 and a mean AMH of 21pmol/L. Of the 580 patients, 44% had a P50nmol/L (CPR 40.6% and 43.6%, respectively, P=0.09; OPR 29.4% and 32.3%; P=0.5; MR 11.5% and 11%; P= 0.9). P level on day of ET was not a predictor of CPR or OPR.
- BMI was negatively correlated with P on day of ET (rTS= -1.48; P100nmol/L.
Before giving the injection, a doctor must wash hands thoroughly to eliminate possible infections, and after washing, hands are cleaned with a clean towel, the cap of a shot is removed and the rubber cap is cleaned with alcohol. The needle is put in the syringe, and it is necessary to avoid touching the needle with your fingers.
The needle is put in the progesterone vial and pulled back so that the predetermined amount of progesterone is sucked into the needle. Progesterone injection is given in the muscular tissue that is in the tights or buttocks. After the injection is given, the needle has to be thrown, since it is no longer supposed to be used.
Side Effects
Side effects of progesterone include nausea, vomiting, and a state of depression during the first few days after the shot is given. If it is given to regulate menstrual periods, side effects such as increased vaginal discharge, pain in the breast area, irritation, and fluid retention may appear.
If it is given in the IVF, stomach pain and cramps in the vaginal area can occur. If the mentioned side effects last for a couple of days, you must immediately pay a visit to the doctor so that he can administer proper treatment.
- www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/progesterone-treatment-does-not-prevent-preterm-birth-twin-pregnancy
- www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/progestin-treatment-polycystic-ovarian-syndrome-may-reduce-pregnancy-chances
- Photo courtesy of Medgirl131 by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Proluton_Depot_%28hydroxyprogesterone_caproate%29_packs.jpg


_f_280x120.jpg)
-Why-Some-Women-Take-This-Type-Of-Progesterone-During-Early-Pregnancy_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...