Introduction and General Data
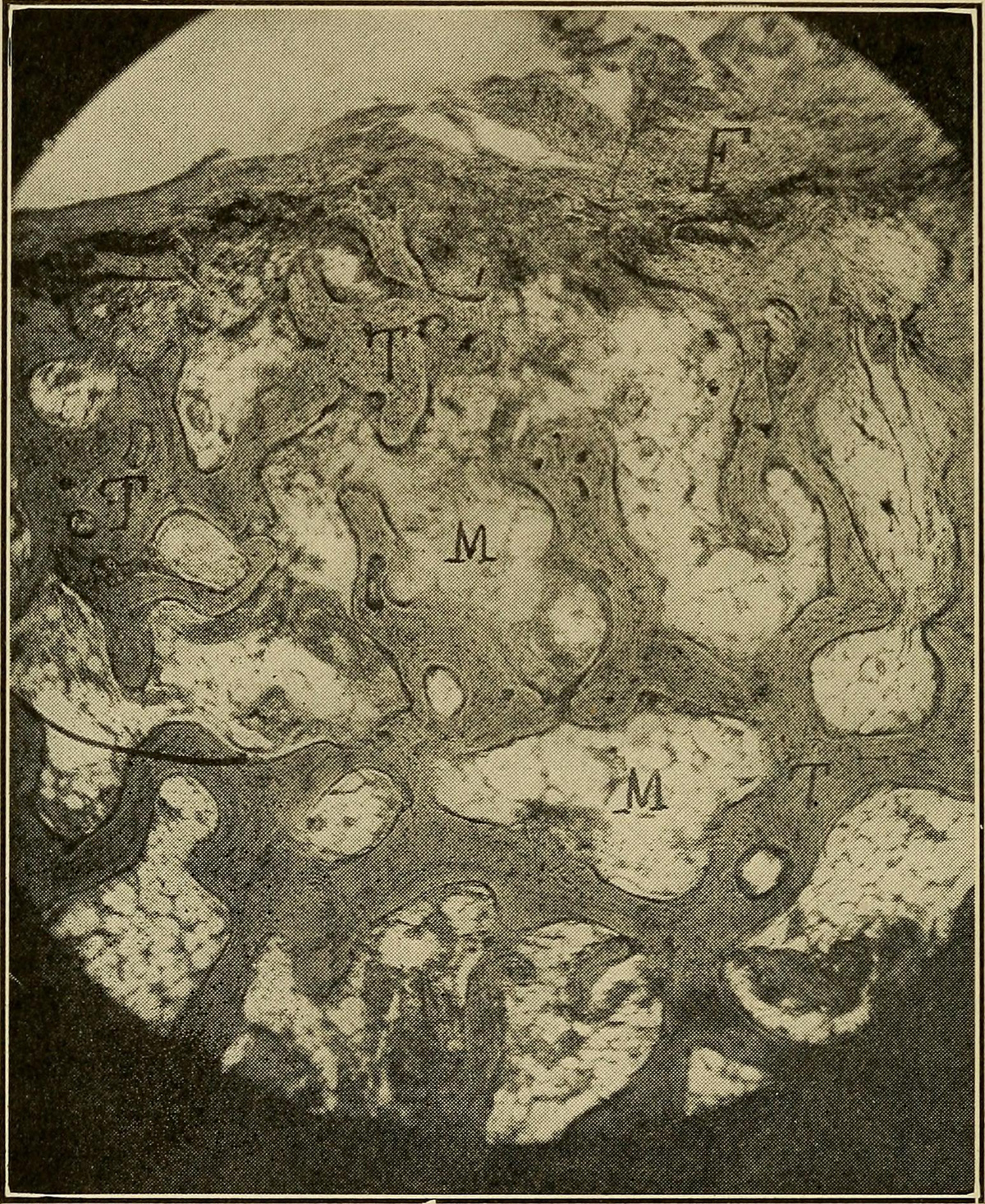
Rheumatoid arthritis is a progressive and chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints. Apart from joints the surrounding tissue may be included in the process as well. Basically the damage to the joints is caused by the production of antibodies. These antibodies attack the cells of the patients and lead to the damage. Even though the disease has chronic course it may be followed by the remission and patients do not have to deal with symptoms and signs of rheumatoid arthritis for a long period of time. There are different medical approaches in treating the disease. However there is no definitive cure for rheumatoid arthritis and unfortunately the majority of patients end up with permanent destruction of the affected joints.
Medication in Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The goal of the medicamentous therapy is to reduce the inflammation of the joints. There are several groups of medications that are administered. They include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, immunosuppressive medications and inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
In mild cases nonsteridal anti-inflammatory medications give excellent results. If the disease is moderate and the patient does not respond to the initial treatment he/ she is given corticosteroids or some of the previously mentioned medications. There is even a possibility of drugs combination. The problem that is regularly present is connected to huge number of side effects that is evident during the medicamentous therapy.
Surgery in Case of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Surgical procedures can be performed in case that patient does not respond to medicamentous therapy. This way the surgery is in charge with repair of the damage. Surgery is highly efficient in restoring the patient's ability to use affected joints again. The surgical procedures that are performed in case of rheumatoid arthritis include complete replacement of the affected joint, repair of tendons, removal of the lining of the affected joints and joint fusion.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Food
There is no specific food which will help with the symptoms and signs of the disease. However, the patient may benefit from certain foods as they will potentially prevent the attack and prolong the period of remission.
Outcome
The very prognosis of the disease depends on the specific case. Some people suffer from the initial attack and never develop symptoms and signs of rheumatoid arthritis again. In other cases the disease turns back and the frequent attacks lead to severe and irreparable damage of the affected joints. Luckily, the therapeutic options are wide and in significant number of patients the disease can be brought under control.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...